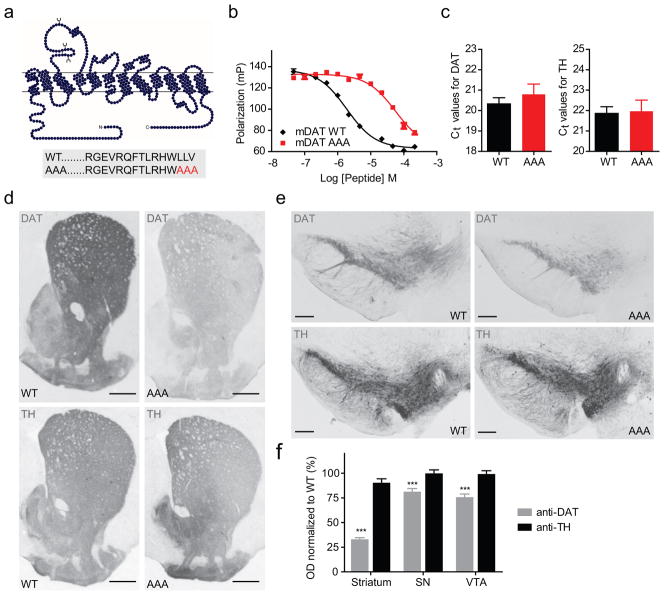
Figure 1. Immunohistochemical characterization of DAT-AAA mice with disrupted C- terminal PDZ-target sequence.
(a) Schematic representation of mDAT topology and C-terminal sequences for WT DAT and DAT-AAA with alanine substitution of three C-terminal residues. (b) Fluorescence polarization competition binding assay on purified PICK1 using 40 nM Oregon Green-labelled human DAT peptide (13 C-terminal residues) and increasing concentration of indicated unlabelled peptides (equivalent to the 13 C-terminal residues of mDAT WT and DAT-AAA). Data are polarization values (mP) (means ± s.e.m., n=3). (c) Quantitative real-time PCR of midbrain tissue from WT and DAT-AAA mice demonstrates no difference in mRNA expression levels. Data are shown as raw cycle threshold (Ct) values for DAT and TH (means ± s.e.m., n=4, non-parametric Mann- Whitney test, P>0.05). (d, e) Representative photomicrographs of DAT-ir and TH-ir in striatum and midbrain from WT and DAT-AAA mice. A substantial loss of DAT-ir is observed in DAT-AAA mice while TH-ir displays similar intensities in both genotypes. (f) Optical densitometry was applied for semi-quantification of DAT and TH levels. Mean values were calculated and values from knock-in mice were normalized to WT (means ± s.e.m., Str = 33%, SN = 81% and VTA = 76% of WT, *** P<0.001, n=5, one-way ANOVA with post-hoc Bonferroni’s multiple comparison test).