Fig. 4.
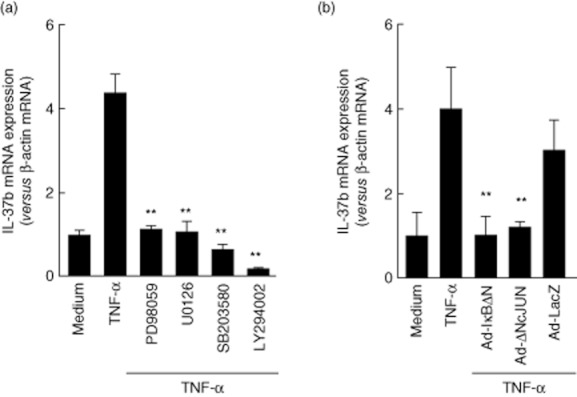
Molecular mechanisms underlying interleukin (IL)-37b mRNA expression. (a) Effects of MAP-and PI3-kinase inhibitors on IL-37b mRNA expression in the intestinal epithelial cell line T84. The cells were pretreated with 10 μM mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase inhibitors (SB203580, PD098059 or U02016) and 10 μM PI3-kinase inhibitor (LY294002) for 15 min each, and then stimulated with tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-α (100 ng/ml) for 24 h. The IL-37b mRNA expression was then determined by real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR). All values are expressed as means ± standard deviation (s.d.) (n = 3). **P < 0·01; a significant difference from the values for TNF-α stimulation. (b) Effects of nuclear factor (NF)-κB and/or activator protein (AP)-1 inhibition on IL-37b mRNA expression. T84 cells were infected with an adenovirus expressing IκBΔN or DN-c-Jun, and at 48 h after infection the cells were stimulated with TNF-α (100 ng/ml) for 24 h. IL-37b mRNA expression was then determined by real-time PCR. All values are expressed as means ± s.d. (n = 3). **P < 0·01; a significant difference from the values for TNF-α stimulation.
