Fig. 6.
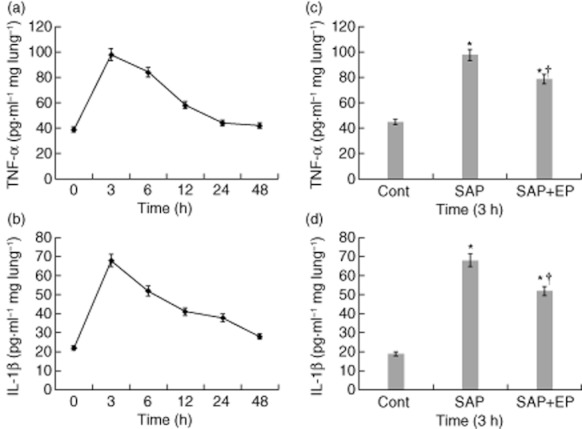
Effects of ethyl pyruvate (EP) treatment on pulmonary tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-α and interleukin (IL)-1β production in pancreatitic rats. (a,b) TNF-α and IL-1β protein of lung in rats was examined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) at the designated time-points after SAP. (c, d) At 3 h after the induction of severe acute pancreatitis (SAP), levels of TNF-α and IL-1β were increased compared with control rats. While SAP rats receiving the treatment with EP had a significant reduction in pulmonary TNF-α and IL-1β expression compared with animals receiving vehicle. The number of rats in each group at every time-point was 12. Values are shown means ± standard error. *P < 0·05 versus control group and †P < 0·05 versus untreated SAP group, as tested by one-way analysis of variance (anova). Cont: control.
