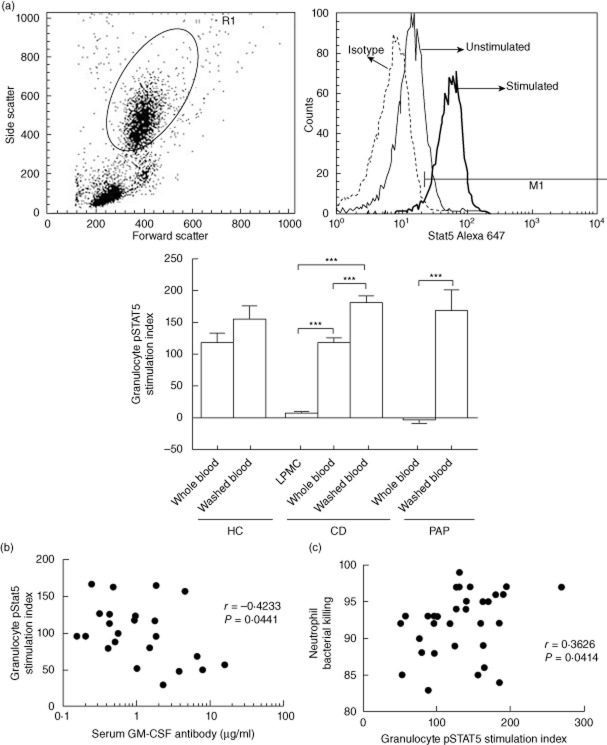
Fig. 4.
Granulocyte–macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) : signal transducter and activator of transcription 5 (STAT5) stimulation index in granulocytes from Crohn disease (CD) patients and healthy and disease controls. The change in intracellular tyrosine phosphorylated STAT5 (pSTAT5) mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) in peripheral granulocytes within whole blood samples, washed blood cells or lamina propria mononuclear cell (LPMC) conditioned media (LPMC) following GM-CSF stimulation was measured by flow cytometry and a pSTAT5 stimulation index was calculated for healthy controls (HC), CD patients, and disease controls with primary alveolar proteinosis (PAP). (a) Representative results for the granulocyte gate and the change in the pSTAT5 MFI with GM-CSF stimulation are shown. Data are shown as the mean (standard error of the mean), differences between groups were compared by t-test or analysis of variance (anova) with Bonferroni's multiple comparison test, ***P < 0·001; n = 11 for HC (healthy controls); n = 9 for CD LPMC conditioned media, n = 55 for CD whole and washed blood, n = 6 for PAP. The association between (b) serum GM-CSF autoantibody concentration and granulocyte pSTAT5 stimulation index (SI) in whole blood (n = 23) and (c) granulocyte pSTAT5 SI and neutrophil bacterial killing (n = 32) was tested by Spearman's correlation.