Figure 4.
IFITM3-VAPA Interaction Is Required to Restrict Viral Entry
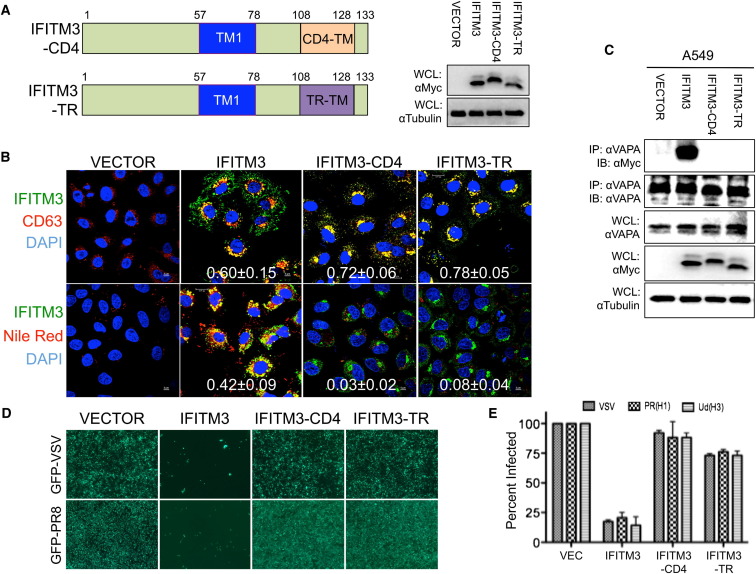
(A) Schematic illustration of IFITM3 chimera carrying the CD4 transmembrane (IFITM-CD4) or transferrin receptor transmembrane (IFITM3-TR). WCLs were used for IB with the indicated antibodies.
(B) A549-Vector, A549-IFITM3, A549-IFITM3-CD4, and A549-IFITM3-TR cells were fixed and stained with anti-Myc (IFITM3), anti-CD63, or Nile Red dye for confocal microscopy. DAPI was used to stain the nucleus. Scale bar, 5 μm. The metric values (mean ± SD) represent the quantitative assessment of the colocalization of CD63 (top panel) and Nile Red (bottom panel) with IFITM3 WT and chimeras (Pearson’s coefficient, mean ± SD, n ≥ 20).
(C) Lysates of A549-Vector, A549-IFITM3, A549-IFITM3-CD4, and A549-IFITM3-TR cells were used for IP and IB. WCLs were used for IB analysis to show expressions of VAPA, IFITMs, and tubulin.
(D) A549-Vector, A549-IFITM3, A549-IFITM3-CD4, and A549-IFITM3-TR cells were infected with GFP-VSV (top panel) or GFP-IAV PR8 (bottom panel). At 48 hr postinfection, cells were photographed under immunofluorescence microscopy (magnification: 4×).
(E) A549-Vector, A549-IFITM3, A549-IFITM3-CD4, and A549-IFITM3-TR cells were infected with defective MLV-EGFP pseudotyped with the envelope proteins of VSV, IAV H1N1 (PR8), or IAV H3N1 (Udorn). Viral entry is expressed as mean EGFP fluorescence relative to vector control cells, as measured by flow cytometry. Values represent mean ± SD, n ≥ 3 independent experiments. See also Figure S4.