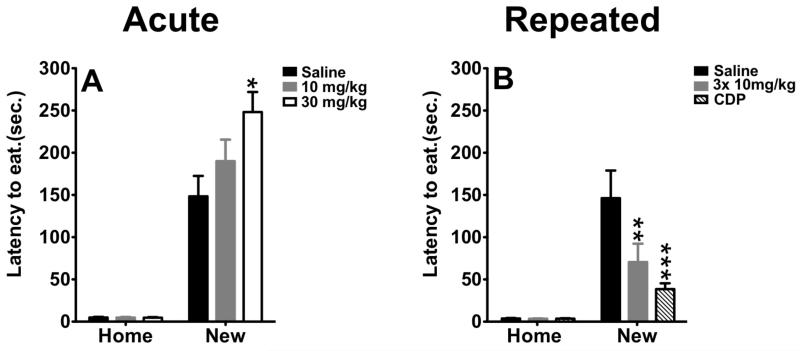
Figure 2. A–B, Sub-chronic, but not acute, administration of citalopram induced anxiolytic-like effects in the novelty-induced hypophagia paradigm.
A) Acute administration of citalopram, at 30 mg/kg but not 10 mg/kg, induced anxiogenic effect in novelty-induced hypopagia (n=9-10, per group). Values are means +/−SEM. * groups that differed significantly from saline treated animals (p<0.05). B) Sub-chronically, citalopram decreased the latency to feed. This effect was comparable to the effects of chlordiazepoxide (n=6-9, per group). Values are means +/−SEM. ** and *** group that differed significantly from vehicle-treated animals (p<0.01, p<0.001, respectively).