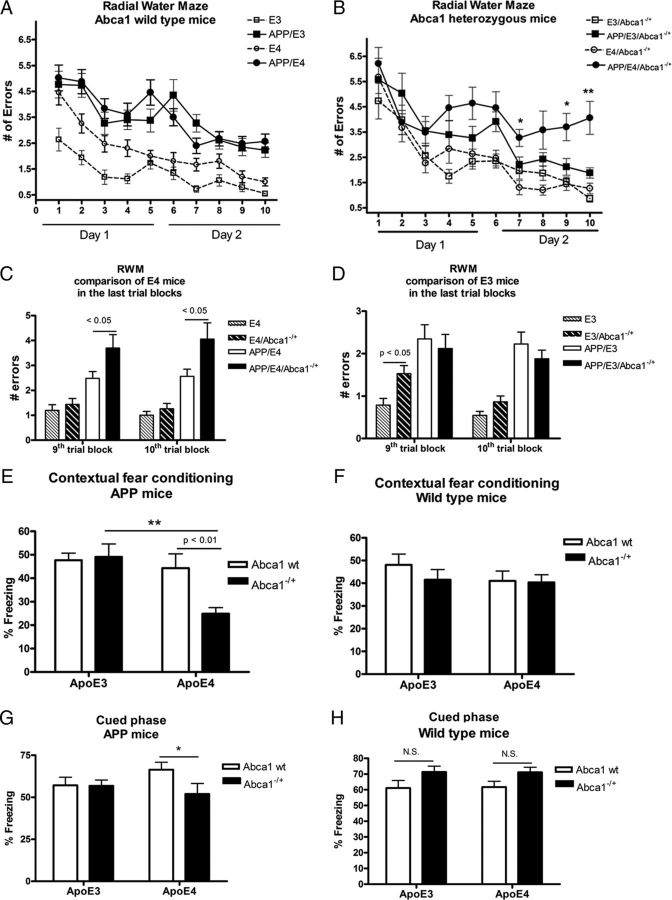
Figure 1.
Abca1 gene dose affects cognitive decline in APP/E4 but not in APP/E3 mice. A–D, RWM was used to assess memory deficits in APP/E3 and APP/E4, as well as in APP/E3/Abca1−/+ and APP/E4/Abca1−/+ mice, between 6 and 8 months of age (mean age, 7.5). Nontransgenic E3, E4, E3/Abca1−/+, and E4/Abca1−/+ mice were used as controls. A, There was no significant difference in cognitive performance between APP/E3 and APP/E4 mice. Analysis by two-way repeated-measures ANOVA demonstrates a significant effect on genotype (p < 0.0001) but no interaction. There was a significant difference between APP transgenic mice and their respective nontransgenic controls. N = 16–25 mice per group. B, RWM revealed a significant difference in cognitive decline between APP/E3/Abca1−/+ and APP/E4/Abca1−/+ mice. Analysis by two-way repeated-measures ANOVA showed an interaction (p < 0.05) and significant effect on genotype (p < 0.0001). There was a significant difference between APP transgenic mice and their respective nontransgenic controls. *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01 when APP/E4/Abca1−/+ were compared with APP/E3/Abca1−/+ by t test. N = 10–17 mice per group. C, The graph shows the performance of all ApoE4 mice on the last two trial blocks. N = 10–22 mice per group. D shows the performance of all ApoE3 mice on the last two trial blocks. N = 11–25 mice per group. In C and D, the two groups were compared by t test. E, F, Contextual fear conditioning paradigm was used to assess memory deficits in younger APP/E3, APP/E4, APP/E3/Abca1−/+, and APP/E4/Abca1−/+ mice (mean age, 4.9 months). Nontransgenic E3, E4, E3/Abca1−/+, and E4/Abca1−/+ age- and gender-matched mice were used as wild-type controls. E, Results for APP mice. Analysis by two-way ANOVA revealed an interaction between Abca1 and ApoE genotype (p < 0.05) and a main effect of ApoE (p < 0.01) but not of Abca1 genotype (p = 0.06). p < 0.01, by Bonferroni's posttest; **p < 0.01 by t test. N = 7–13 per group. F, Results from contextual fear conditioning for wild-type mice. Analysis by two-way ANOVA showed no interaction and no main effects of Abca1 and ApoE. No significant difference between APP mice and their non-APP controls except for APP/E4/Abca1−/+, which differed significantly from E4/Abca1−/+ (APP/E4/Abca1−/+ percentage freezing, 24.89 ± 2.56, vs E4/Abca1−/+ percentage freezing, 40.31 ± 3.40; p < 0.01 by t test). N = 15–20 mice per group. G, Cued phase of fear conditioning test was performed on the same APP/E3, APP/E4, APP/E3/Abca1−/+, and APP/E4/Abca1−/+ mice as in E. Analysis by two-way ANOVA showed no interaction and no main effects of Abca1 and ApoE. **p < 0.01 by t test; N = 7–13 per group. H, Cued phase of fear conditioning test was performed on the same wild-type controls as in F. N.S., Not significant. N = 15–20 mice per group. Error bars indicate SEM.