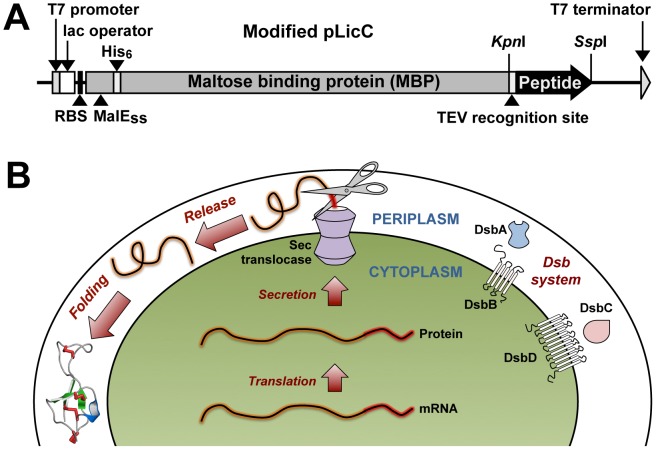
Figure 1. Design of expression vector.
(A) Schematic representation of the pLic-MBP expression vector using for periplasmic expression of disulfide-rich peptides in E. coli. The coding region includes a MalE signal sequence (MalESS) for targeting the fusion protein to the periplasm, a His6 tag for affinity purification, a MBP fusion tag to aid solubility, and a codon-optimised gene encoding the target peptide, with a TEV protease recognition site inserted between the MBP and target-peptide coding regions. The locations of key elements of the vector are shown, including the upstream ribosome binding site (RBS), T7 promoter, lac operator, and key restriction sites. (B) Schematic of the periplasmic expression system for production of disulfide-rich peptides in E. coli. After translation, the fusion protein is transported to the periplasm via the Sec translocase system [89]. The MalE signal sequence (red tube) is removed during this process, releasing the fusion protein (orange tube) into the periplasm where the Dsb machinery (DsbA, DsbB, DsbC, and DsbD) can assist with disulfide-bond formation.