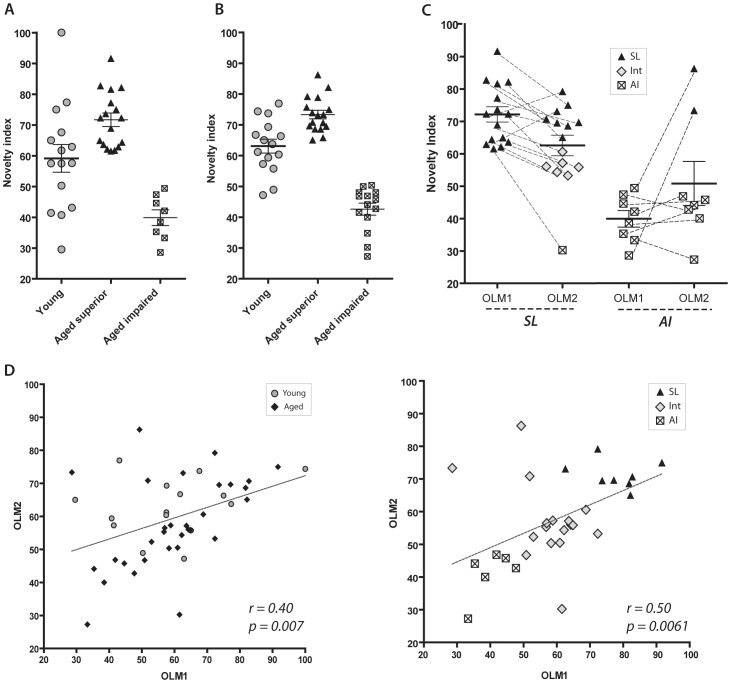
Figure 2. Statistical analysis shows a significant correlation between individual performance on OLM1 and OLM2.
Data shown as novelty index, or proportion of total investigation time spent attending to the object in the novel location. (A) First round of OLM (OLM1) [young, n = 15; SL, n = 17; AI, n = 8]. (B) Second round of OLM (OLM2) using the same animals [young, n = 15; SL, n = 17; AI, n = 14]. Aged performance groups on OLM2 are delineated without reference to previous performance on OLM1. (C) For animals ranked as SL or AI on OLM1, a dotted line connects that individual’s performance on OLM1 to their performance on OLM2 (see also Table 1). Only animals classified as SL or AI on OLM1 are shown, and their classification on OLM2 are shown as SL = black triangles, AI = white squares, and intermediates = grey diamonds. (D) Correlation analysis between individual performance on OLM1 and OLM2. Young = grey circles, aged = black diamonds (n = 44, all young, SL, AI, and Intermediate animals included). (E): Correlation analysis for the aged rats. Grey diamonds indicate animals that were categorized differently in OLM1 and OLM2, or were classified as Intermediate in both tests. For details on this group of animals please refer to Tables 1 and 2.