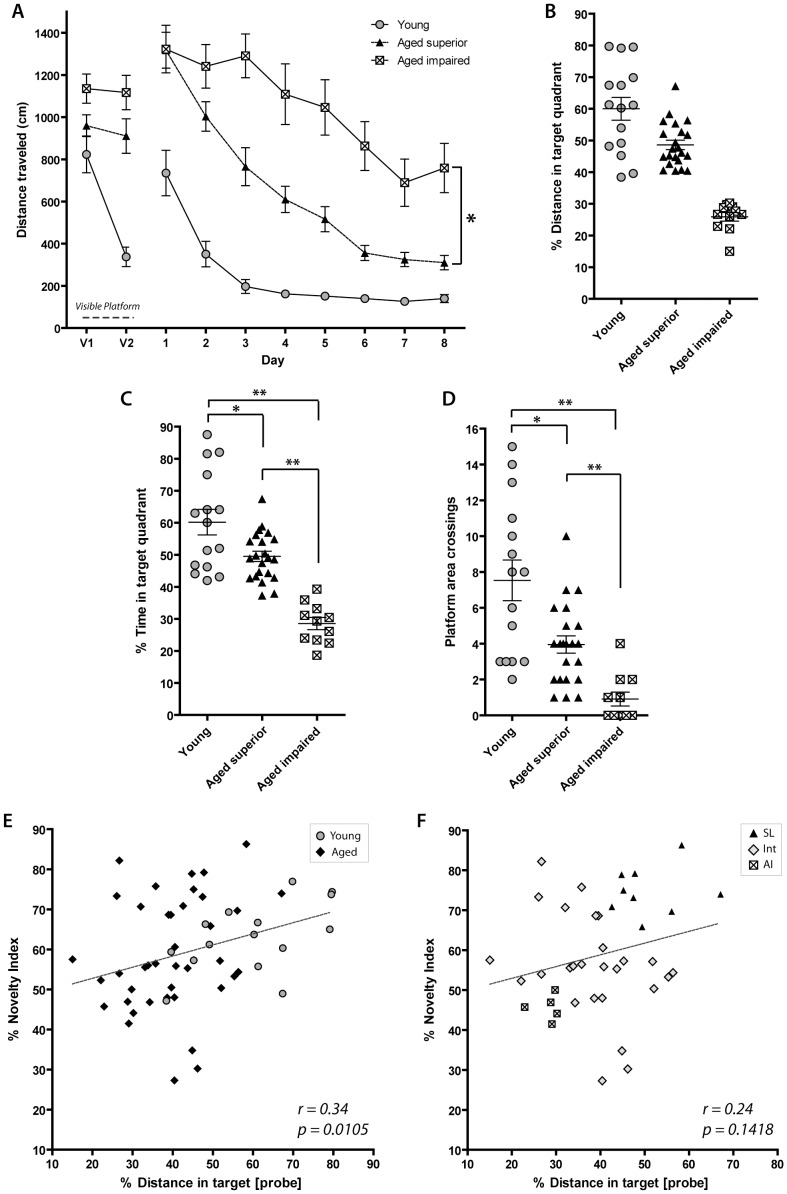
Figure 3. Performance on OLM correlates with performance on the MWM probe trial.
(A) Task acquisition on the MWM in young and aged rats, four trials per day. The first eight trials (Days 1 & 2) represent the visual version of the task. Young animals learn the task quickly, although aged superior learners learn the task soon afterward. Aged impaired learners do not show high acquisition of the task. Asterisk indicates a significant difference of AI and SL performance on the MWM over time. (B) Percent of total swim distance spent in target quadrant during probe trial (Day 10) was the criterion by which animals were grouped into SL, AI, or intermediate. Both young and SL animals cover >40% of their total swim distance in the target quadrant. AI animals perform close to the chance level (25%). (C) Percent of total time spent in the target platform during probe trial show significant differences performance between SL, AI and young rats. (D) Platform crossings during probe trial show statistical differences in performance between SL, AI and young rats. (E) Individual novelty index on OLM2 significantly correlates to performance on the probe trial of the MWM when young (grey circles) and aged groups (black diamonds) are included (n = 55, young, SL, AI, and intermediate animals included). [Young, n = 15; SL, n = 22; AI, n = 11, and intermediate, n = 7, as defined by % total target swim distance]. (F): Correlation analysis for the aged rats. Grey diamonds indicate animals that were categorized differently in OLM2 and MWM, or were classified as intermediate on both. For details on these groups of animals, please refer to Tables 2 and 3.