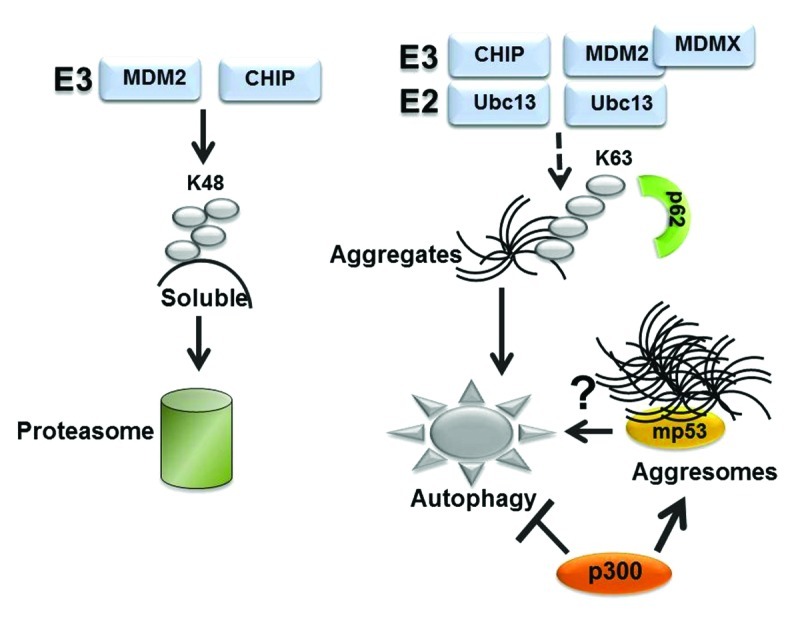
Figure 5. Hypothetical role played by the ubiquitin code in proteasomal or autophagic degradation (see also text for explanation). While substrates modified by K48-linked ubiquitin chains are recognized by the proteasome, K63 chain formation is involved in a variety of other functions, including in the autophagic clearance of micro- or macro-aggregates. CHIP can catalyze K63 ubiquitination when in combination with Ubc13. In the case of MDM2 K63 chain formation required MDMX.37 We speculate that K63-linked ubiquitin chains may play a role in autophagic disruption of mutant p53. Other studies have shown that mutant p53 localize in aggresomes, wherein misfolded proteins are either stored or cleared by autophagy.31 The observation that p300 inhibits autophagy44 and is necessary for aggresome formation43 raises the possibility that autophagic degradation of mutant p53 within aggresomes is regulated by the interaction with p300.
