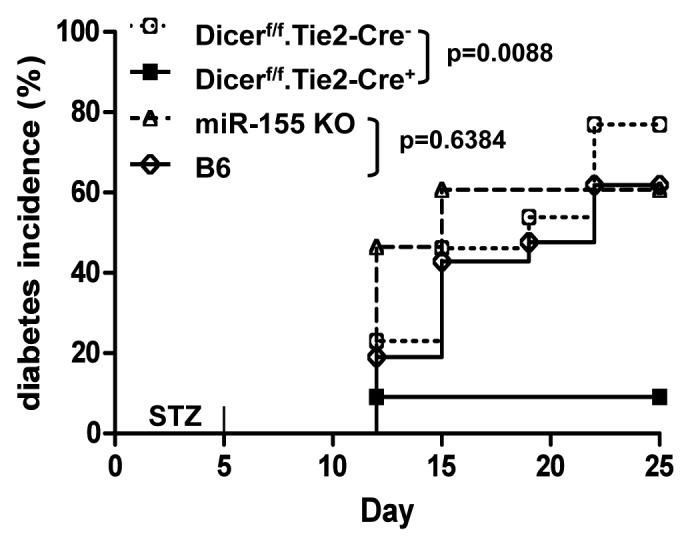
Figure 1. Deletion of microRNAs in bone marrow prevents streptozotocin-induced murine autoimmune diabetes, but deletion of miR-155 does not. Seven–9-week-old male Dicerf/f.Tie2-cre+ KO (■) and Dicerf/f.Tie2-cre- WT (○) mice, miR-155KO (∆) and B6 WT (◊) controls were injected intraperitoneally with freshly dissolved STZ (50 mg/kg) (Sigma) for 5 consecutive days. Development of glucosuria was monitored with Clinistix (Bayer Diagnostics). Clinical diabetes is defined by positive glucosuria and hyperglycemia (blood glucose levels > 250 mg/dl) on two consecutive days in nonfasting animals. Mice were followed until 25 d after the last injection of STZ. Data shown here is a combination (n = 11–28) of two to three experiments.
