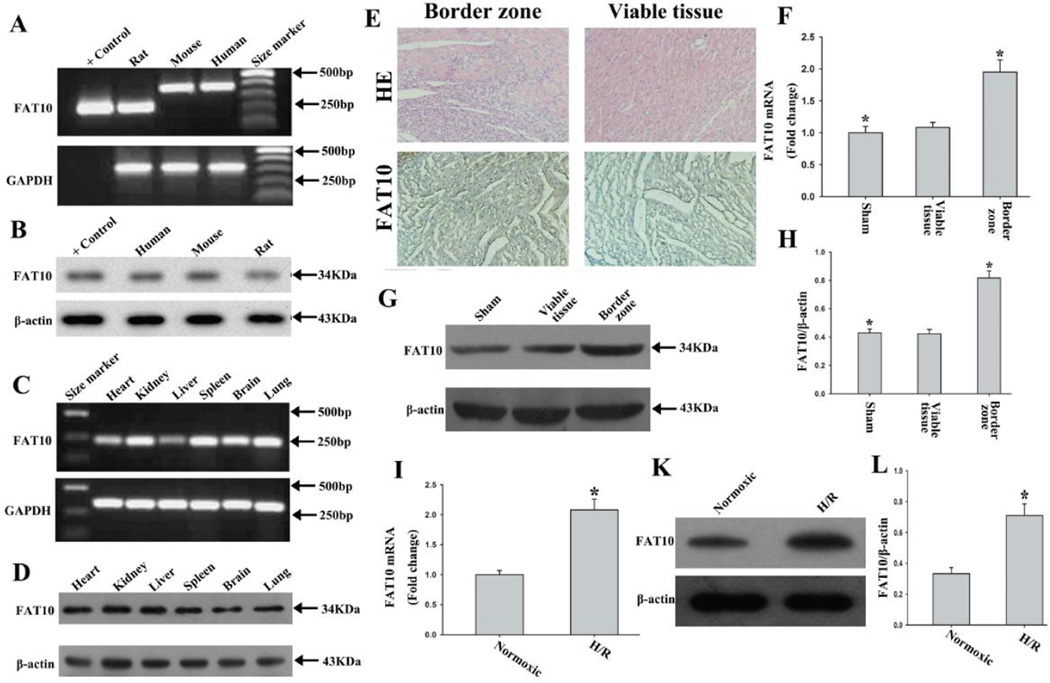
Figure 1. Expression of FAT10 in the heart and its up-regulation in response to ischemia.
A. Detection of expression of Fat10 mRNA by RT-PCR and agarose gel electrophoresis in human, mouse and rat hearts, as identified by the label in each lane. The expected products, based on the design of PCR primers, were 180bp for rat Fat10 cDNA, 360bp for mouse Fat10 cDNA and 366bp for human FAT10 cDNA. Positive control group used the construction of vector expressing rat Fat10 cDNA as template. GADPH served as an internal control.
B. FAT10 protein, detected in myocardial tissues from rat, mouse and human, by Western blotting. Positive control group used proteins from 293T cells after transfection the vector expressing rat Fat10 cDNA. β-actin is used as a control for loading conditions.
C-D. Expression of FAT10 mRNA in different rat tissues as detected by RT-PCR, and western blot showing expression of FAT10 protein. Tissue source of RNA and protein are indicated above the panel. GADPH is used as an internal control for mRNA expression and β-actin is used as a control for loading conditions for protein expression.
E. Representative images of rat heart sections stained with H&E and immunocytochemistry from the sham-operated group and the MI group respectively. FAT10 is distributed abundantly in the border zone of myocardial infraction. Bar: 10 µm
F. Bar graph showing Fat10 mRNA level was significantly increased in the border zone of myocardial infarction as compared with sham-operated rats. The data were compared to the Gapdh level and normalized to the mean value of controls, n=6, * P<0.05 compared to sham-operated group.
G. Expression of FAT10 protein in heart tissues of sham and MI rats, as detected by Western blotting. β-actin is used as a loading control.
H. Quantitative analysis of FAT10 protein level in control and ischemic border zone, (n=3 experiments for each groups). *P<0.05 vs. sham-group.
I -K. Illustrate changes in Fat10 mRNA, as detected by qPCR (I), and FAT10 protein level as detected by Western blotting (K) and quantitative data (H) in cultured cardiac myocytes exposed to hypoxia. β-actin is used as a control for loading conditions. Quantitative analysis is in right panels (n=3 experiments for each groups). *P < 0.05 compared to normoxic condition.