Figure 2. Beyond IL-1β.
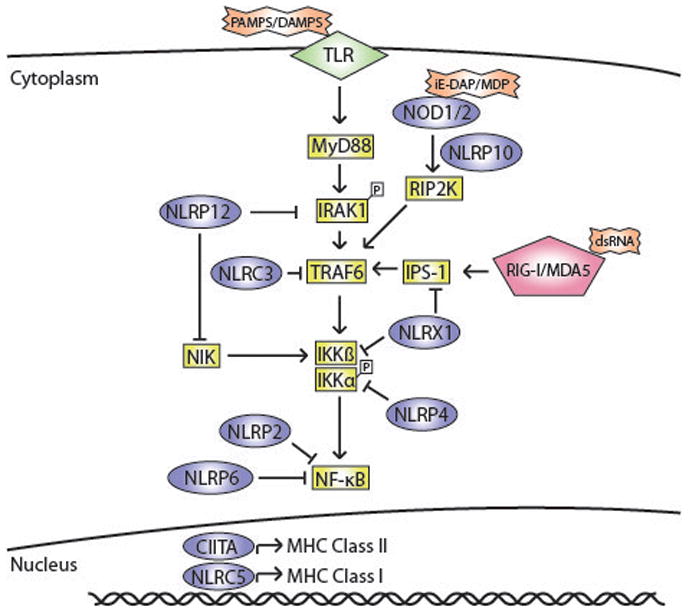
Apart from inflammasomes, NLRs play different roles in modulating DC function. Certain NLRs regulate signalling cascades initiated by other pattern recognition receptors like TLRs and RIG-I/MDA-5. NOD1/2 activation synergistically amplifies TLR-mediated activation of NF-κB thus leading to enhanced DC maturation. Other NLRs negatively regulate NF-κB activation by TLRs and RIG-I/MDA-5. NLRP12, NLRX1 and NLRP4 have been shown to bind and inhibit the activity of specific proteins involved in inflammatory signalling cascades. NLRP2 and NLRP6 have also been shown to impair NF-κB activation but the exact mechanism is yet to be elucidated. Additionally, NLRs like CIITA and NLRC5 can control dendritic cell maturation by transcriptional regulation of MHC Class I and Class II respectively.
