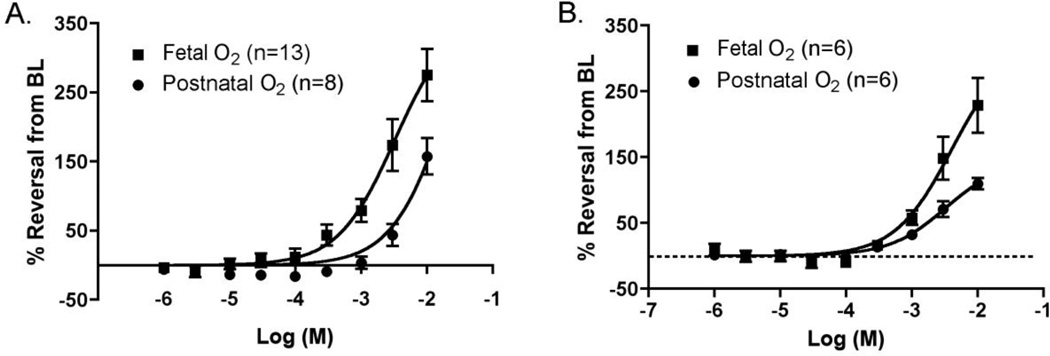
Figure 3. Response of the isolated mouse DA to cimetidine.
A. Relaxation of the term gestation (d19) DA under fetal or postnatal oxygen (O2) conditions in the perfusion bath. B. Relaxation of the preterm gestation (d15) DA under fetal or postnatal oxygen conditions. Each dose-response curve shows significant concentration-dependent DA relaxation (p<0.01) compared to the preconstricted baseline (BL) diameter. In d19 mice, relaxation was significantly greater in fetal oxygen conditions than in postnatal oxygen conditions (p<0.01). This difference was not significant in d15 mice (p=0.567). DA relaxation was significantly greater with d19 mice than d15 mice for either fetal oxygen conditions (p<0.01) or for postnatal oxygen conditions (p=0.01). Thus, cimetidine-induced DA relaxation is dependent on cimetidine concentration, gestational maturation, and oxygen level.