Figure 6. c-Jun suppresses AR function in castration-resistant prostate cancer cells.
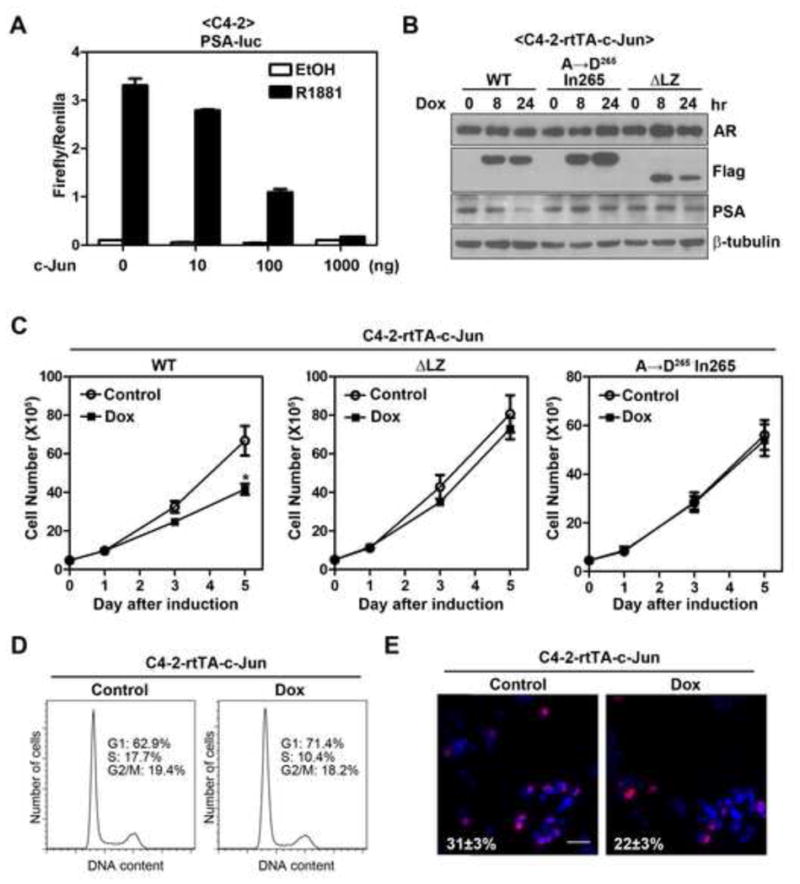
(A) Effect of c-Jun overexpression on R1881-induced PSA promoter activity in C4-2 cells. PSA reporter assay was performed in C4-2 cells using method as described in Figure 1A. Error bars, S.E. (n=3). (B) Induction of c-Jun inhibits endogenous PSA expression in C4-2 cells. C4-2-rtTA-c-Jun cells (wild-type or mutants) were treated with 100 ng/ml of doxycycline (Dox) for indicated periods of time. AR, PSA and Flag-c-Jun (Flag) proteins were immunoblotted. (C) Overexpression of c-Jun reduces cell number of C4-2 cells. Effects of c-Jun (wild-type or mutants) induction on cell number of C4-2 cells were determined using the method as describe in Figure 5A. The asterisk indicates a significant difference (P<0.05) when compared with the control group (student’s t-test). Error bars, S.E. (n=4 for c-Jun or c-JunΔLZ; n=3 for c-Jun A→D265 In265). (D) Effect of c-Jun overexpression on cell cycle progression of C4-2 cells. C4-2-rtTA-c-Jun cells were treated with or without Dox for 3 days, followed by flow cytometry analysis of cell cycle progression. (E) Effect of c-Jun overexpression on DNA synthesis of C4-2 cells. C4- 2-rtTA-c-Jun cells were treated with or without Dox for 3 days and followed by Brdu incorporation assay. Shown are representative merged images of BrdU labeling (red) DAPI staining (blue). Bar, 100 μm. The number indicates the percentage of Brdu incorporated cells±S.E.
