Figure 7. Lipidomic results.
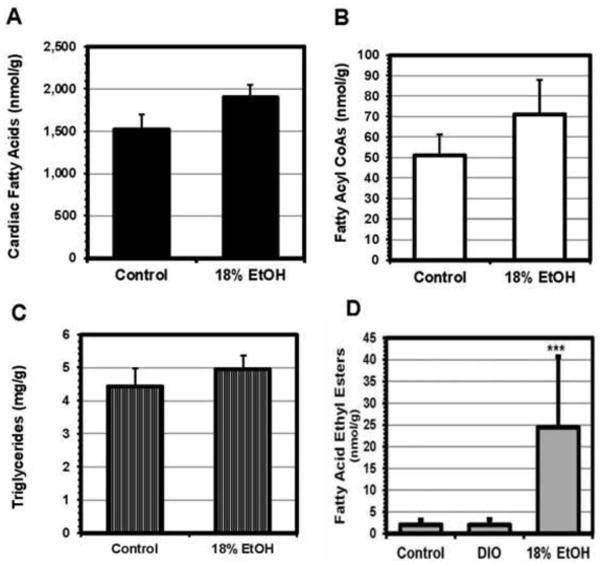
LC/MS/MS measurements of the cardiac content of key components of the fatty acid pathway in EtOH-fed mice. Total fatty acids (A), fatty acyl CoAs (B), and triglycerides (C) were all increased in the EtOH-fed mice compared to controls, although only the increase in fatty acids was statistically significant. In addition, fatty acid ethyl esters (FAEEs), a cardiotoxic non-oxidative metabolite of EtOH metabolism, were increased by a mean of 12-fold in the E18 group (D). The analysis employed resolved 11 different FAEEs; all were increased in the EtOH-treated animals.
