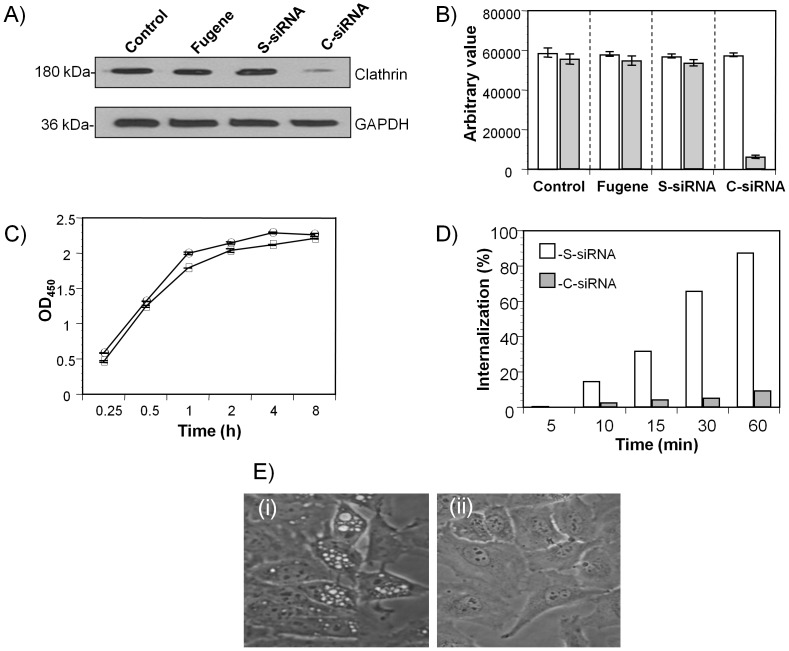
Figure 5. Clathrin-rCARDS toxin association.
(A) Small interfering RNA (siRNA) mediated gene silencing of clathrin heavy chain. HeLa cells were transfected with clathrin heavy chain targeted siRNA (C-siRNA) or scrambled siRNA (S-siRNA) as described in Materials and Methods. Twenty-four h after the second siRNA transfection, cells were lysed and clathrin expression was analyzed using anti-clathrin (1∶500) or anti-GAPDH (1∶2000) antibodies as detailed in Materials and Methods and described in this legend. (B) Quantification of clathrin heavy chain expression in C-siRNA- and S-siRNA-treated HeLa cells. Clathrin and GAPDH band intensities were estimated using KODAK 1D Image analysis software, and results are from three independent experiments. (C) Binding of rCARDS toxin in clathrin-depleted cells. S-siRNA-treated (open square) and C-siRNA-treated (open circle) HeLa cells were incubated with 10 µg/ml of rCARDS toxin for 1 h at 4°C, and toxin binding was analyzed as described in Materials and Methods. Data are means ±SD values from two triplicate experiments. (D) Internalization of rCARDS toxin in clathrin-depleted HeLa cells. S-siRNA-treated (white bar) and C-siRNA-treated (gray bar) HeLa cells were incubated with 10 µg/ml of Biotin-CARDS toxin for 1 h at 4°C and shifted to 37°C for 1 h. After removing surface-bound biotin with MESNA, internalized rCARDS toxin was measured as described in Materials and Methods. (E) Clathrin effect on rCARDS toxin-mediated vacuole formation. S-siRNA-treated (i) and C-siRNA-treated (ii) HeLa cells were incubated with 50 µg/ml of rCARDS toxin for 24 h at 37°C and analyzed under light microscopy for vacuole formation as described previously [14].