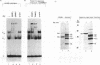Abstract
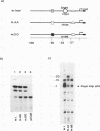
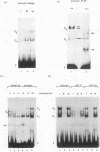
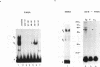
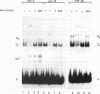
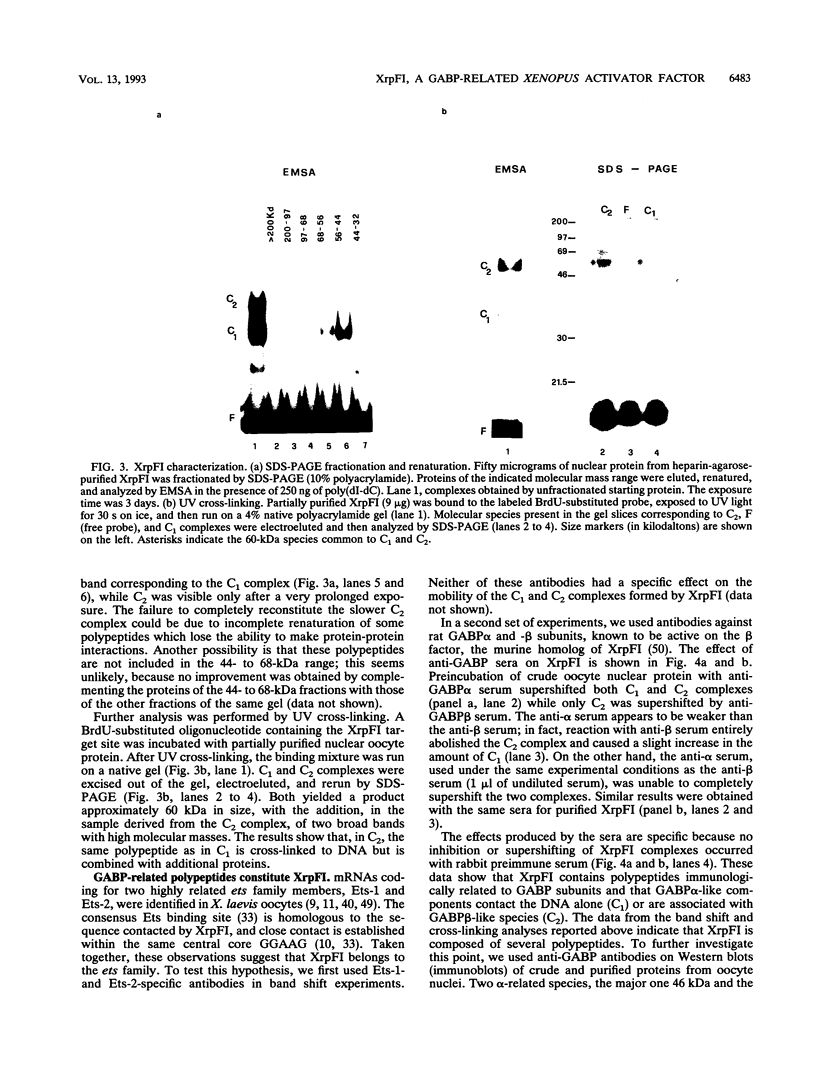
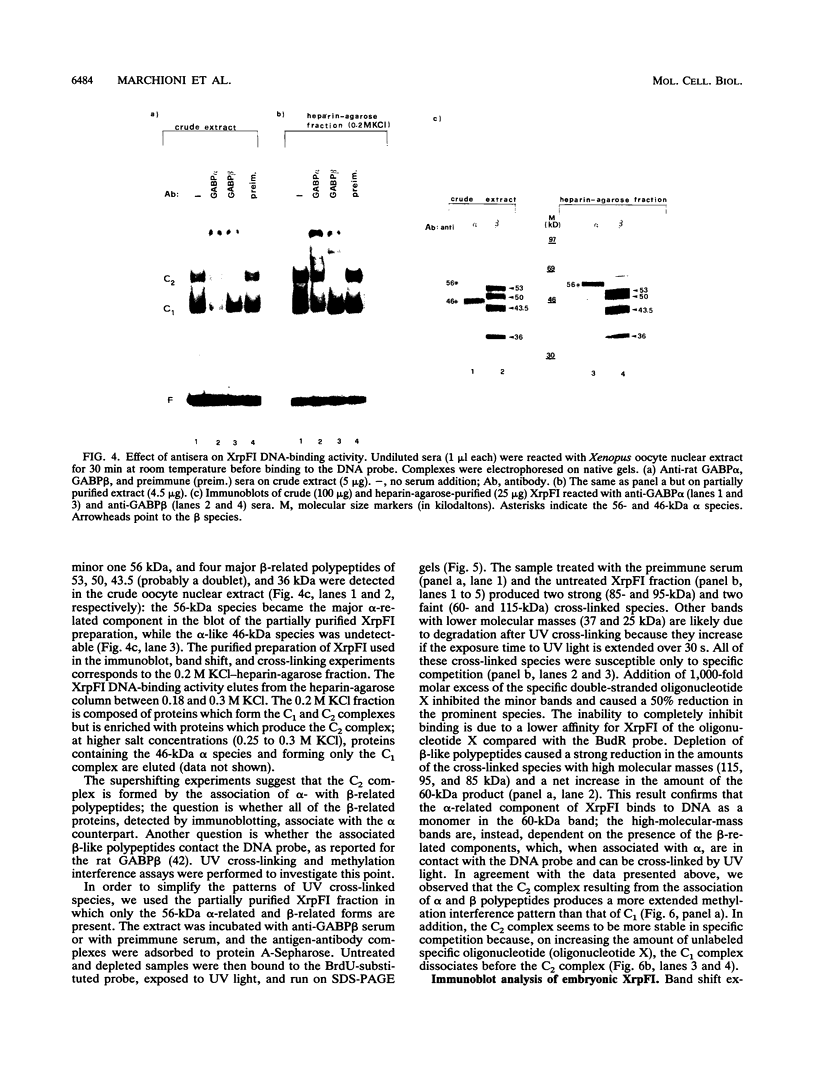
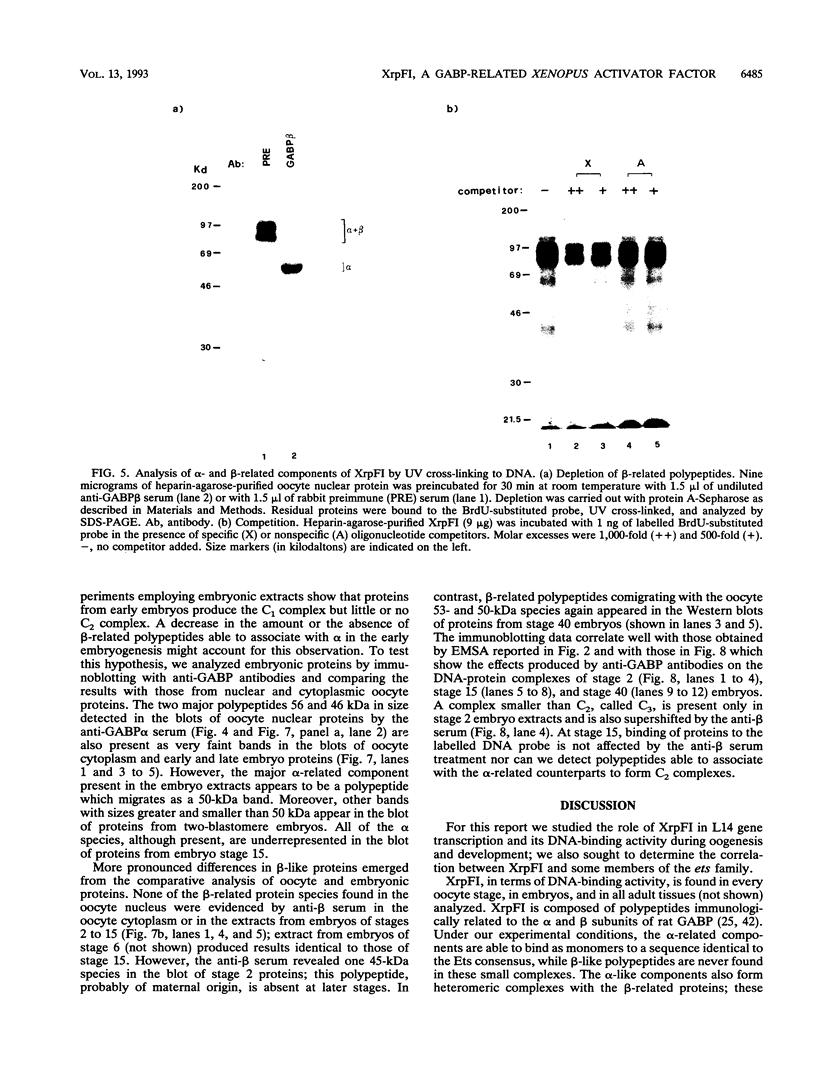
XrpFI, first identified in the extract of Xenopus laevis oocyte nuclei, binds to a proximal sequence of the L14 ribosomal protein gene promoter. Its target sequence, 5'-TAACCGGAAGTTTGT-3', is required to fully activate the promoter, and the two G's of the central motif are essential for factor binding and transcriptional activation; our data also suggest that XrpFI may play a role in cap site positioning. The binding site of XrpFI is homologous to the sequence recognized by the family of ets genes. Antibodies specific for Ets-1 and Ets-2 proteins did not react with XrpFI, but those raised against the rat alpha and beta GA-binding proteins both supershifted the retarded bands formed by XrpFI. The Xenopus polypeptides related to GA-binding protein alpha interact with DNA both as monomers and as heterodimers associated with beta-related proteins. Oocyte nuclei contain multiple forms of alpha- and beta-related proteins: the alpha-like proteins remain throughout development, while the pattern of the beta species changes in the embryonic stages examined. beta-like proteins are undetectable in the cleavage period up to the neurula stage, but at later stages, when ribosomal protein genes are actively transcribed, two beta-related polypeptides reappear.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BROWN D. D., LITTNA E. RNA SYNTHESIS DURING THE DEVELOPMENT OF XENOPUS LAEVIS, THE SOUTH AFRICAN CLAWED TOAD. J Mol Biol. 1964 May;8:669–687. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80116-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baeuerle P. A., Baltimore D. Activation of DNA-binding activity in an apparently cytoplasmic precursor of the NF-kappa B transcription factor. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):211–217. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90382-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beccari E., Mazzetti P., Mileo A., Bozzoni I., Pierandrei-Amaldi P., Amaldi F. Sequences coding for the ribosomal protein L14 in Xenopus laevis and Xenopus tropicalis; homologies in the 5' untranslated region are shared with other r-protein mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Oct 10;14(19):7633–7646. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.19.7633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-David Y., Giddens E. B., Letwin K., Bernstein A. Erythroleukemia induction by Friend murine leukemia virus: insertional activation of a new member of the ets gene family, Fli-1, closely linked to c-ets-1. Genes Dev. 1991 Jun;5(6):908–918. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.6.908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhat N. K., Fisher R. J., Fujiwara S., Ascione R., Papas T. S. Temporal and tissue-specific expression of mouse ets genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3161–3165. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown T. A., McKnight S. L. Specificities of protein-protein and protein-DNA interaction of GABP alpha and two newly defined ets-related proteins. Genes Dev. 1992 Dec;6(12B):2502–2512. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.12b.2502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burdett L. A., Qi S., Chen Z. Q., Lautenberger J. A., Papas T. S. Characterization of the cDNA sequences of two Xenopus ets-2 proto-oncogenes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jan 25;20(2):371–371. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.2.371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carnevali F., La Porta C., Ilardi V., Beccari E. Nuclear factors specifically bind to upstream sequences of a Xenopus laevis ribosomal protein gene promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Oct 25;17(20):8171–8184. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.20.8171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Z. Q., Burdett L. A., Seth A. K., Lautenberger J. A., Papas T. S. Requirement of ets-2 expression for Xenopus oocyte maturation. Science. 1990 Dec 7;250(4986):1416–1418. doi: 10.1126/science.2255913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumont J. N. Oogenesis in Xenopus laevis (Daudin). I. Stages of oocyte development in laboratory maintained animals. J Morphol. 1972 Feb;136(2):153–179. doi: 10.1002/jmor.1051360203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. Control of eukaryotic messenger RNA synthesis by sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins. 1985 Aug 29-Sep 4Nature. 316(6031):774–778. doi: 10.1038/316774a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutman A., Wasylyk B. Nuclear targets for transcription regulation by oncogenes. Trends Genet. 1991 Feb;7(2):49–54. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90231-E. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutman A., Wasylyk B. The collagenase gene promoter contains a TPA and oncogene-responsive unit encompassing the PEA3 and AP-1 binding sites. EMBO J. 1990 Jul;9(7):2241–2246. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07394.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hariharan N., Kelley D. E., Perry R. P. Equipotent mouse ribosomal protein promoters have a similar architecture that includes internal sequence elements. Genes Dev. 1989 Nov;3(11):1789–1800. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.11.1789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hariharan N., Perry R. P. Functional dissection of a mouse ribosomal protein promoter: significance of the polypyrimidine initiator and an element in the TATA-box region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(4):1526–1530. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.4.1526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karim F. D., Urness L. D., Thummel C. S., Klemsz M. J., McKercher S. R., Celada A., Van Beveren C., Maki R. A., Gunther C. V., Nye J. A. The ETS-domain: a new DNA-binding motif that recognizes a purine-rich core DNA sequence. Genes Dev. 1990 Sep;4(9):1451–1453. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.9.1451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemsz M. J., McKercher S. R., Celada A., Van Beveren C., Maki R. A. The macrophage and B cell-specific transcription factor PU.1 is related to the ets oncogene. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):113–124. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90219-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaMarco K., Thompson C. C., Byers B. P., Walton E. M., McKnight S. L. Identification of Ets- and notch-related subunits in GA binding protein. Science. 1991 Aug 16;253(5021):789–792. doi: 10.1126/science.1876836. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagna G., Loreni F., Beccari E., Carnevali F. HrpF, a human sequence-specific DNA-binding protein homologous to XrpFI, a Xenopus laevis oocyte transcription factor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 11;18(19):5811–5816. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.19.5811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai Z. C., Rubin G. M. Negative control of photoreceptor development in Drosophila by the product of the yan gene, an ETS domain protein. Cell. 1992 Aug 21;70(4):609–620. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90430-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leprince D., Gegonne A., Coll J., de Taisne C., Schneeberger A., Lagrou C., Stehelin D. A putative second cell-derived oncogene of the avian leukaemia retrovirus E26. Nature. 1983 Nov 24;306(5941):395–397. doi: 10.1038/306395a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Goodbourn S., Fischer J. A. Regulation of inducible and tissue-specific gene expression. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1237–1245. doi: 10.1126/science.3296191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui T., Segall J., Weil P. A., Roeder R. G. Multiple factors required for accurate initiation of transcription by purified RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11992–11996. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Kingsbury R. Transcriptional control signals of a eukaryotic protein-coding gene. Science. 1982 Jul 23;217(4557):316–324. doi: 10.1126/science.6283634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunn M. F., Seeburg P. H., Moscovici C., Duesberg P. H. Tripartite structure of the avian erythroblastosis virus E26 transforming gene. Nature. 1983 Nov 24;306(5941):391–395. doi: 10.1038/306391a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nye J. A., Petersen J. M., Gunther C. V., Jonsen M. D., Graves B. J. Interaction of murine ets-1 with GGA-binding sites establishes the ETS domain as a new DNA-binding motif. Genes Dev. 1992 Jun;6(6):975–990. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.6.975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierandrei-Amaldi P., Campioni N., Beccari E., Bozzoni I., Amaldi F. Expression of ribosomal-protein genes in Xenopus laevis development. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):163–171. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90022-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M. Gene regulation by proteins acting nearby and at a distance. Nature. 1986 Aug 21;322(6081):697–701. doi: 10.1038/322697a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy E. S., Rao V. N., Papas T. S. The erg gene: a human gene related to the ets oncogene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(17):6131–6135. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.17.6131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds G. A., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. Multiple mRNAs for 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase determined by multiple transcription initiation sites and intron splicing sites in the 5'-untranslated region. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 25;260(18):10369–10377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scotto K. W., Kaulen H., Roeder R. G. Positive and negative regulation of the gene for transcription factor IIIA in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Genes Dev. 1989 May;3(5):651–662. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.5.651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiegler P., Wolff C. M., Baltzinger M., Hirtzlin J., Senan F., Meyer D., Ghysdael J., Stéhelin D., Befort N., Remy P. Characterization of Xenopus laevis cDNA clones of the c-ets-1 proto-oncogene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Sep 11;18(17):5298–5298. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.17.5298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson C. B., Wang C. Y., Ho I. C., Bohjanen P. R., Petryniak B., June C. H., Miesfeldt S., Zhang L., Nabel G. J., Karpinski B. cis-acting sequences required for inducible interleukin-2 enhancer function bind a novel Ets-related protein, Elf-1. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;12(3):1043–1053. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.3.1043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson C. C., Brown T. A., McKnight S. L. Convergence of Ets- and notch-related structural motifs in a heteromeric DNA binding complex. Science. 1991 Aug 16;253(5021):762–768. doi: 10.1126/science.1876833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urness L. D., Thummel C. S. Molecular interactions within the ecdysone regulatory hierarchy: DNA binding properties of the Drosophila ecdysone-inducible E74A protein. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):47–61. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90287-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virbasius J. V., Virbasius C. A., Scarpulla R. C. Identity of GABP with NRF-2, a multisubunit activator of cytochrome oxidase expression, reveals a cellular role for an ETS domain activator of viral promoters. Genes Dev. 1993 Mar;7(3):380–392. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.3.380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang W., Gralla J. D., Carey M. The acidic activator GAL4-AH can stimulate polymerase II transcription by promoting assembly of a closed complex requiring TFIID and TFIIA. Genes Dev. 1992 Sep;6(9):1716–1727. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.9.1716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk B., Wasylyk C., Flores P., Begue A., Leprince D., Stehelin D. The c-ets proto-oncogenes encode transcription factors that cooperate with c-Fos and c-Jun for transcriptional activation. Nature. 1990 Jul 12;346(6280):191–193. doi: 10.1038/346191a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk C., Gutman A., Nicholson R., Wasylyk B. The c-Ets oncoprotein activates the stromelysin promoter through the same elements as several non-nuclear oncoproteins. EMBO J. 1991 May;10(5):1127–1134. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08053.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson D. K., McWilliams M. J., Lapis P., Lautenberger J. A., Schweinfest C. W., Papas T. S. Mammalian ets-1 and ets-2 genes encode highly conserved proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):7862–7866. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.7862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff C. M., Stiegler P., Baltzinger M., Meyer D., Ghysdael J., Stéhelin D., Befort N., Remy P. Isolation of two different c-ets-2 proto-oncogenes in Xenopus laevis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Aug 11;18(15):4603–4604. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.15.4603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xin J. H., Cowie A., Lachance P., Hassell J. A. Molecular cloning and characterization of PEA3, a new member of the Ets oncogene family that is differentially expressed in mouse embryonic cells. Genes Dev. 1992 Mar;6(3):481–496. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.3.481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoganathan T., Bhat N. K., Sells B. H. A positive regulator of the ribosomal protein gene, beta factor, belongs to the ETS oncoprotein family. Biochem J. 1992 Oct 15;287(Pt 2):349–353. doi: 10.1042/bj2870349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]