Figure 1.
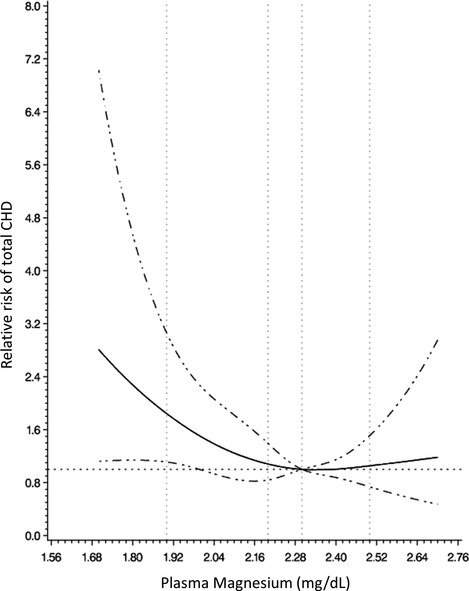
Multivariate relative risk of total CHD as a function of plasma magnesium. Data were fitted by a restricted cubic spline Cox proportional hazards model. The 95% confidence intervals are indicated by dashed lines. Models conditioned on matching factors (age, smoking status, month of blood draw, and fasting status) and adjusted for BMI, exercise, alcohol intake, family history of MI, eGFR, menopausal therapy, multivitamin use, intake of omega‐3 fats, polyunsaturated:saturated fat, trans fat, dietary cholesterol, cereal fiber, calcium, potassium, vitamin D, magnesium, baseline hypertension, baseline hypercholesterolemia, baseline diabetes, and concentration of HDL‐C, LDL‐C, hsCRP, adiponectin, and HbA1c. CHD indicates coronary heart disease; BMI, body mass index; MI, myocardial infarction; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; HDL‐C, high‐density lipoprotein cholesterol; LDL‐C, low‐density lipoprotein cholesterol; hsCRP, high‐sensitivity C‐reactive protein; HbA1c, hemoglobin A1c.
