Figure 2.
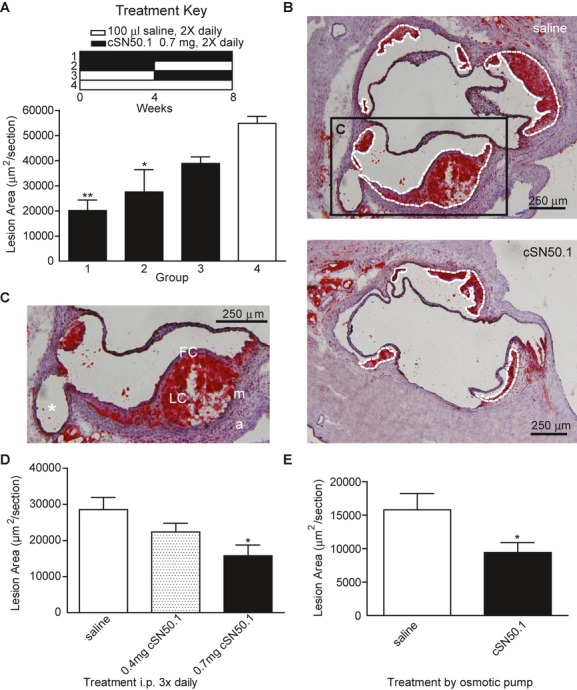
Atherosclerosis is reduced in Western diet–fed ldlr−/− mice treated with NTM. A, Six‐week‐old ldlr−/− mice (n=5/group) were treated with 0.7 mg/mouse cSN50.1 by intraperitoneal injection for 8 weeks twice daily (group 1) or for either the first 4 weeks (group 2) or last 4 weeks (group 3). Control mice were given an equivalent volume of saline twice daily for the entire 8 weeks (group 4). See treatment key in (A). Average lesion area was determined by Oil‐red‐O analysis of the aortic sinus (*P<0.05 and **P<0.005 by Kruskal–Wallis with a Dunn's multiple‐comparison posttest). B, Representative sections of the aortic sinus stained with Oil‐red‐O to detect neutral lipids. Sections are from mice treated for 8 weeks with saline (group 4) or cSN50.1 (group 1) while being fed a Western diet. White dashed lines depict the area used to quantify lesion size. As illustrated, lesion area was not measured past the internal elastic lamina, and the tunica media or adventitia was not included. Inset box C delineates the area magnified to show relevant structures in the plaque. C, The ostia to a coronary artery (*), lipid core (LC), fibrous cap (FC), tunica media (m) and tunica adventitia (a) are identified. Scale bar represents 250 μm in (B) and (C). D, Reduction of atherosclerosis in Western diet–fed ldlr−/− mice treated with NTM was dose dependent. Mice receiving 0.7 mg/mouse of cSN50 peptide 3 times daily by intraperitoneal injection for 4 weeks (n=5/group) had a significant reduction in atherosclerotic lesion size compared with the saline‐treated group. Mice that received 0.4 mg/mouse 3 times daily were not protected from atherosclerosis (*P<0.05 by Kruskal–Wallis with a Dunn's multiple‐comparison posttest). E, Six‐week‐old ldlr−/− mice treated with saline (n=11) or cSN50.1 (n=17) delivered by osmotic pump for 4 weeks (*P<0.05 by Mann–Whitney test). Shown are mean+SEM in (A), (D), and (E). NTM indicates nuclear transport modifier; ldlr−/−, low‐density lipoprotein receptor deficient.
