Figure 5.
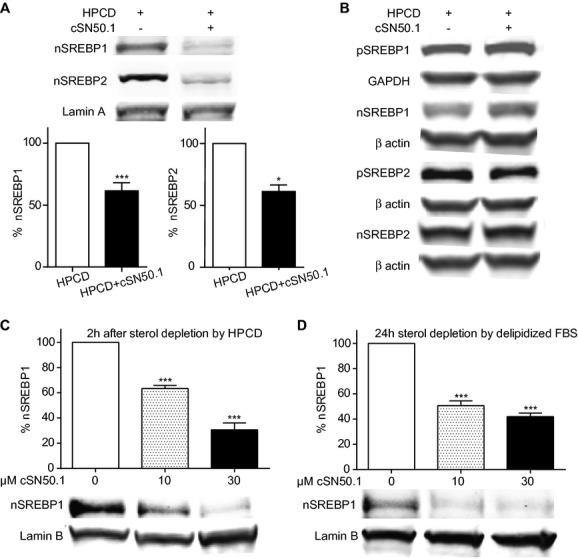
NTM inhibits nuclear translocation of SREBPs in sterol‐depleted HepG2 cells. Nuclear and cytosolic extracts were immunoblotted with antibodies to SREBP1 and SREBP2. For normalization, nuclear extracts were also immunoblotted with anti‐Lamin A/C or Lamin B, whereas cytosolic extracts were normalized to GAPDH or β actin immunoblot controls as indicated. All lanes shown in each row are from the same membrane for each primary antibody, and the same membrane was blotted for the appropriate loading control protein unless otherwise indicated. Values from sterol‐depleted samples without cSN50.1 treatment were set to 100%, and percent values for peptide‐treated samples were calculated. The difference represents percent inhibition of nuclear translocation by cSN50.1 shown as the mean±SEM of ≥3 independent experiments. A and B, Cells incubated with hydroxypropyl‐β‐cyclodextrin (HPCD) for 15 minutes, then treated with 0 or 30 μmol/L cSN50.1 in DMEM+5% delipidized FBS for 2 hours. A, Nuclear extracts (*P<0.05 and ***P<0.0005 by Student's t test). Shown is a representative Lamin A control immunoblot. B, Cytosolic extracts. Statistical analyses of values from cytosolic extracts in 4 experiments (SREBP1) or 3 experiments (SREBP2) showed no significant differences (by Student's t test) between precursor (pSREBPs) outside the nucleus. A significant increase of mature, cleaved SREBP1 (nSREBP1) is apparent in the same cytosolic extracts (P<0.05 by Student's t test), though cytosolic nSREBP2 is not significantly increased. C and D, Concentration‐dependent inhibition of SREBP1 normalized to Lamin in sterol‐depleted HepG2 cells. C, Rapid depletion of sterols with HPCD as in (A). D, Gradual depletion of sterols in cells treated with 0, 10, or 30 μmol/L cSN50.1 in DMEM+5% delipidized FBS only for 24 hours (***P<0.0005 by 1‐way ANOVA with a Tukey's multiple‐comparison posttest). NTM indicates nuclear transport modifier; SREBP, sterol regulatory element‐binding protein; FBS, fetal bovine serum; ANOVA, analysis of variance.
