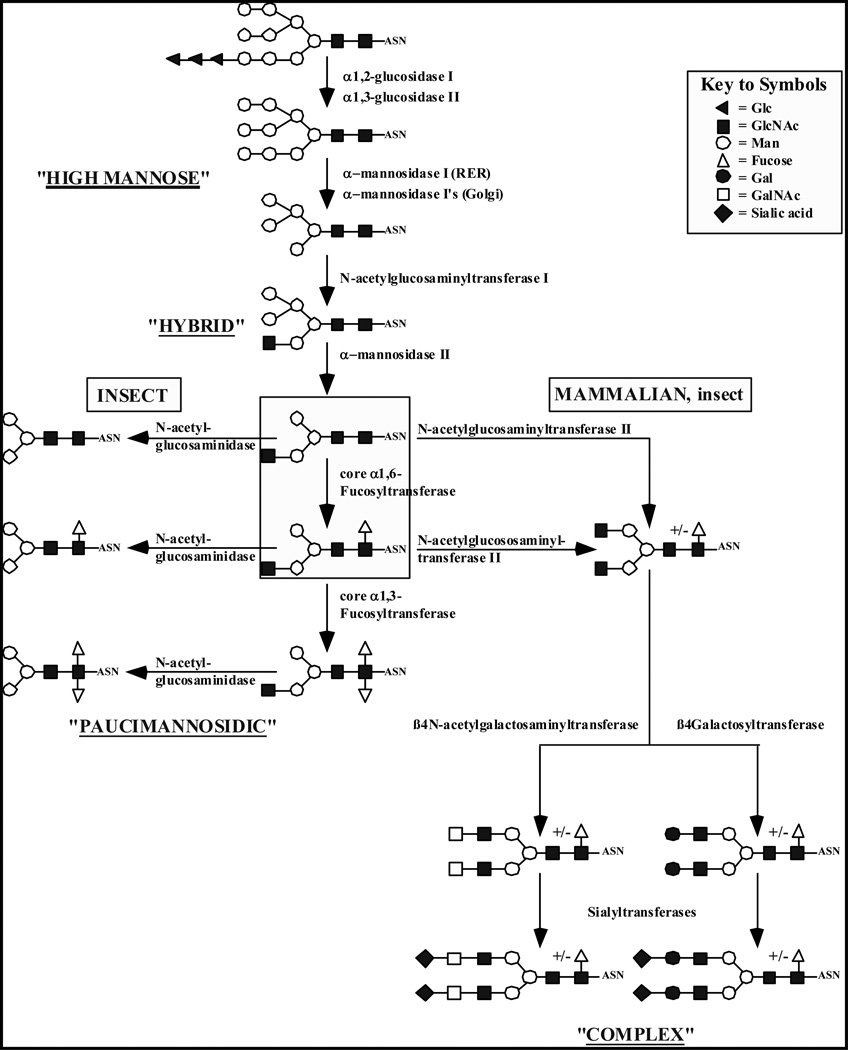
Fig. (1). Protein N-glycosylation pathways in insect and mammalian cells.
Monosaccharides are designated by their standard symbols, as defined in the key. The boxed N-glycans are the last common intermediates in the insect and mammalian pathways. The major insect cell products are paucimannosidic N-glycans with or without core fucose residues, as shown on the far left-hand side of the Figure. The major mammalian cell products are complex, terminally sialylated N-glycans, such as the biantennary N-glycans shown on the bottom right-hand side of the Figure. The Figure also accommodates the potential ability of insect cells to produce more extensively processed N-glycans like those produced by mammalian cells.