Figure 5.
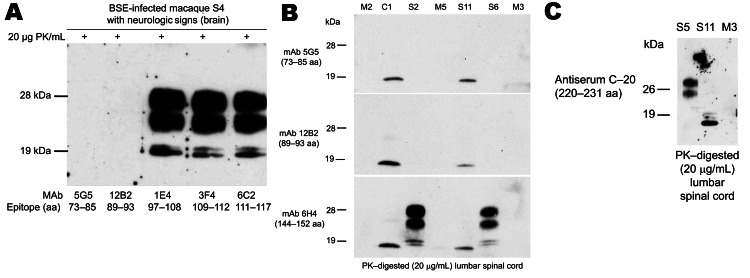
A) Epitope mapping of proteinease-resistant prion protein (PrPres) by Western immunblot analyses (thalamus) from a macaque showing neurologic signs. The PK-sensitive N terminal fragment (mAb 5G5) and the adjacent region showing a variable PK sensitivity (mAb 12B2) were completely digested by the proteinease. MAbs 1E4, 3F4, and 6C2 detected the PrPres triplet termed type 2B signature. B) Epitope mapping of PrPres by Western blot analyses (lumbar spinal cord segment L2) in clinically ill (S2, S6), subclinical (C1), and preclinical (S11) macaques. In preclinical macaques, mAbs 5G5, 12B2, and 6H4 detected a 17 kDa PrPres fragment. Tissue samples from mock (M) controls were completely negative for PrPres. C) Epitope mapping of PrPres by Western blot analyses (lumbar spinal cord segment L2) in a clinically ill macaque (S5), a preclinical macaque (S11), and a non–BSE-infected age-/sex-matched control macaque (M3). PK-treated tissue homogenates from preclinical macaques could also be immunostained with antiserum C20 directed against the C-terminus of the atypical 17-kDa fragment. BSE, bovine spongiform encephalopathy; PK, proteinase K; mAb, monoclonal antibody; M2, M3, M5, noninfected macaques.
