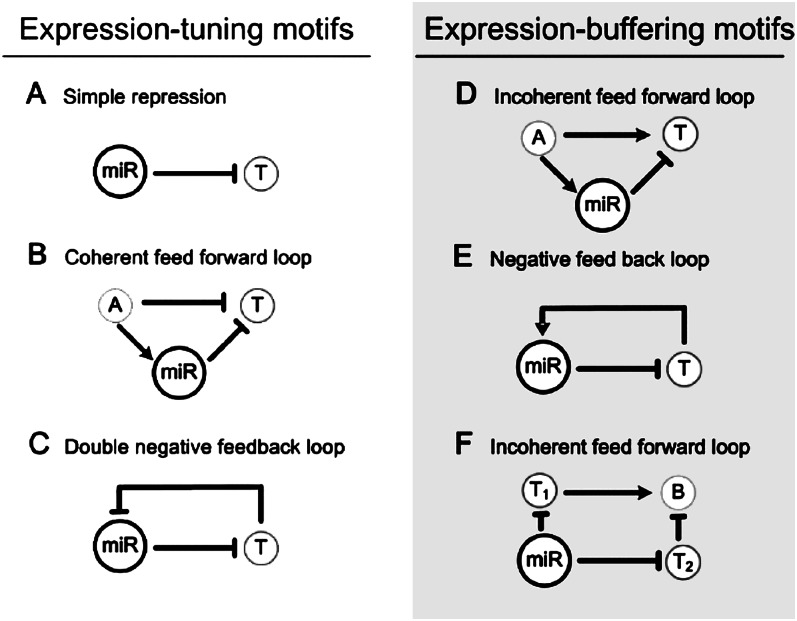
Figure 1.
Simple network motifs containing miRNA. T denotes the target gene of miRNA; A and B denote other genes. These motifs are classified according to the functions in either tuning or buffering. The expression-tuning motifs include: (A) Simple repression in which miRNA reduces the expression of T; (B) coherent feed-forward loop, where miRNA reinforces the repression of T; (C) double-negative feedback loop, where miRNA and T mutually repress each other. The repression of T and expression of miR, or vice versa, is reinforced by the feedback. This is referred to as a “bistable” motif. The expression-buffering motifs include: (D) incoherent feed-forward loop (FFL), where miRNA buffers the expression of T against the fluctuation in A. (E) Negative feedback loop, where miR and T mutually buffer each other's expression from perturbation. (F) Incoherent FFL with four nodes, in which T1 and T2 buffer gene B against fluctuations in miR.