Figure 3. Bladder-contained infections fail to evoke significant antibody responses unless primary immunity was already established.
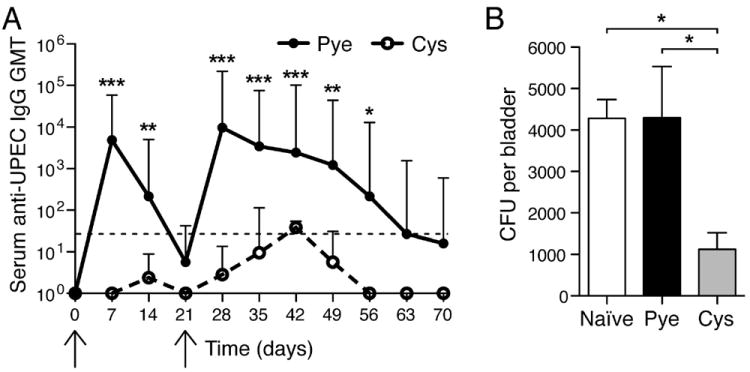
(A) Mice were infected transurethrally with 1×108 CFU to induce cystitis-only or pyelonephritis (first arrow) and serum GMT anti-UPEC antibodies were measured (x-axis shows days p.i.). On day 21 (second arrow) cystitis-only was induced in both groups. *p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001, compared to naïve. Error bars represent the 95% confidence level with n=4-7. Dotted line denotes threshold of detection. (B) Naïve mice that were adoptively transferred splenocytes from mice that previously had acute pyelonephritis show enhanced bacterial clearance 5d post-cystitis challenge, compared to control naïve mice or mice adoptively transferred splenocytes from mice that previously had cystitis only. *p<0.05. Error bars represent ±SEM with n=4-6.
