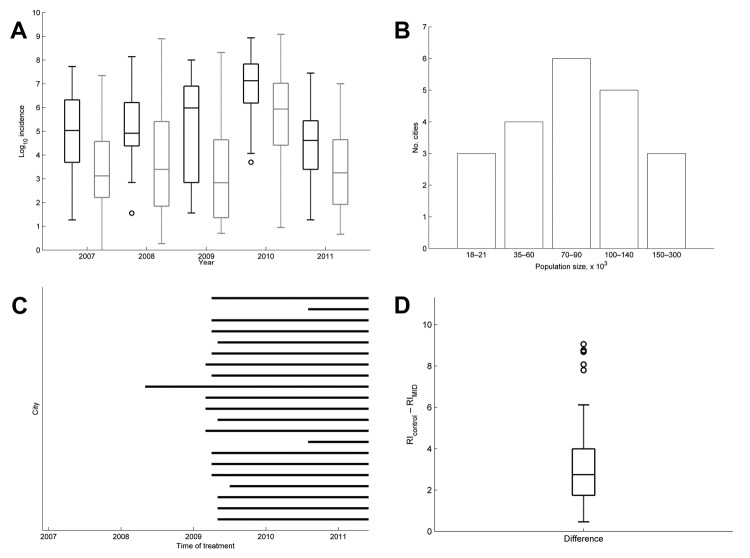
Figure 2.
Changes in incidence of dengue fever in 21 cities that implemented Monitoramento Inteligente da Dengue (Intelligent Dengue Monitoring System [MID]), Minas Gerais, Brazil, mid-January 2007–June 2011. A) Annual incidence in 21 cities that implemented MID (bars outlined in black) and 147 cities that had not implemented MID (bars outlined in gray). Horizontal lines in boxplots indicate medians of 1,000 medians. Whiskers indicate ± 2.7 SD. Circles indicate points that fall outside ± 2.7 SD. B) Distribution of population sizes in cities that implemented MID. C) Time that MID was implemented in each city. D) Median relative increase (RI) in incidence for cities that implemented MID versus cities that had not implemented MID. RI was calculated as the sum of monthly incidence after MID was implemented divided by the sum of monthly incidence before MID was implemented for the same number of months. For cities that implemented MID, the median is a single value for the 21 cities. For cities that had not implemented MID, 21 cities with the same distribution of population sizes as MID cities were selected at random 1,000 times and their median relative differences during the same set of time frames were calculated. Horizontal line in the boxplot indicates median of 1,000 medians. Whiskers indicate ± 2.7 SD. Circles indicate points that fall outside ± 2.7 SD.