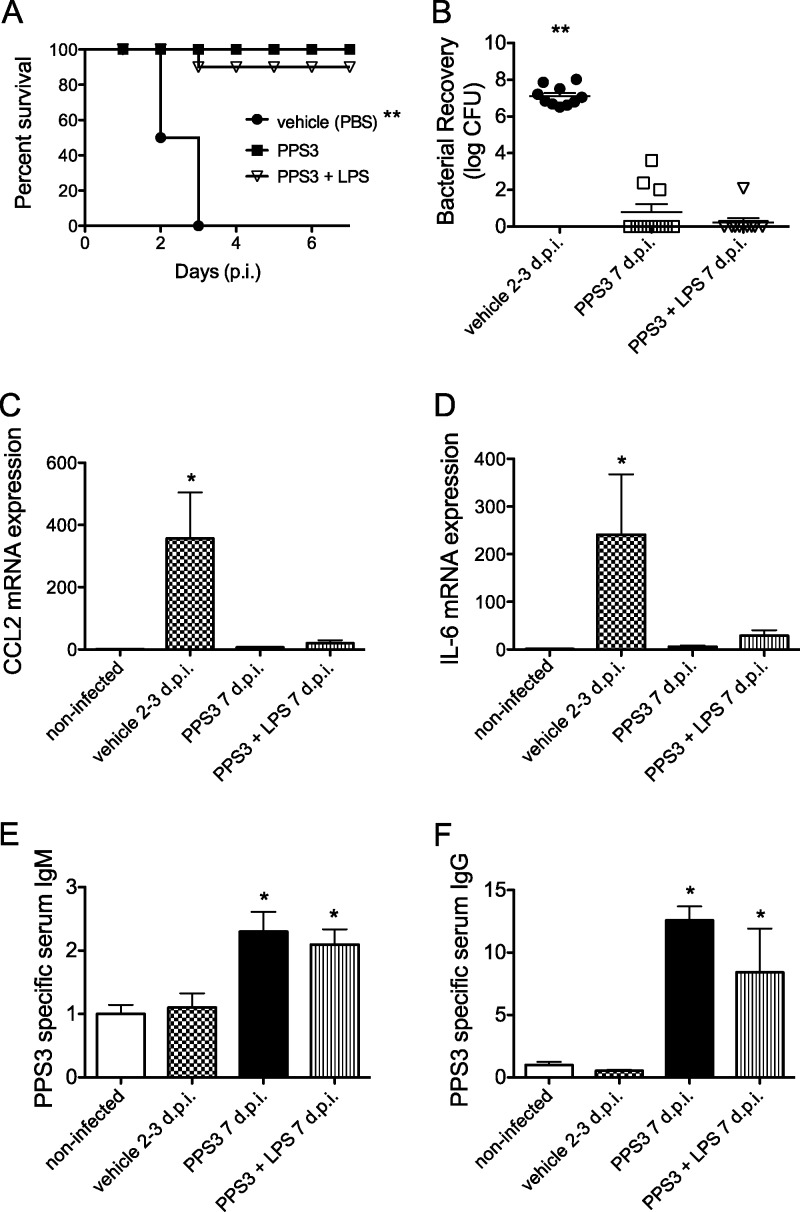
Fig 3.
Immunization with PPS3 and PPS3+LPS promotes survival and resolution of pneumococcal challenge. Vehicle (PBS)-immunized, PPS3-immunized, and coimmunized mice (n = 10 per group) were inoculated with 5 × 104 CFU at 5 days after immunization and monitored for 1 week for survival. (A) Kaplan-Meier survival curve is shown. **, P < 0.0001 as determined by log-rank Mantel-Cox test. (B) Lungs (n = 10 per group) from vehicle-immunized mice at 2 to 3 days p.i. (d p.i.) and from PPS3- and PPS3+LPS-immunized mice at 7 days p.i. were homogenized, serially diluted, and plated to determine bacterial load. **, P < 0.0001, by a Student's t test in comparison to vehicle-immunized, infected controls. (C and D) Lung cytokine mRNA expression levels at 2 to 3 days (vehicle, n = 5) and 7 days (PPS3, n = 10; PPS3+LPS, n = 5) p.i. were assessed by Q-PCR, and results were analyzed by the ΔΔCT method. Expression levels are shown as fold change in comparison to baseline noninfected values. (E and F) Blood was collected from noninfected mice, from vehicle-immunized, infected mice at 2 to 3 days p.i. and from and PPS3- and PPS3+LPS-immunized, infected mice at 7 days p.i.; PPS3-specific IgM and IgG serum levels were determined by ELISA. Serum IgM and IgG (n = 7/group) levels are depicted as fold change in the optical density values relative to those of the noninfected controls. Asterisks denote P values of <0.05 (*) and <0.0001 (**) as determined by one-way ANOVA with Tukey's posthoc test in comparison to infected control values. Data from survival studies represent three separate in vivo pneumonia infections.