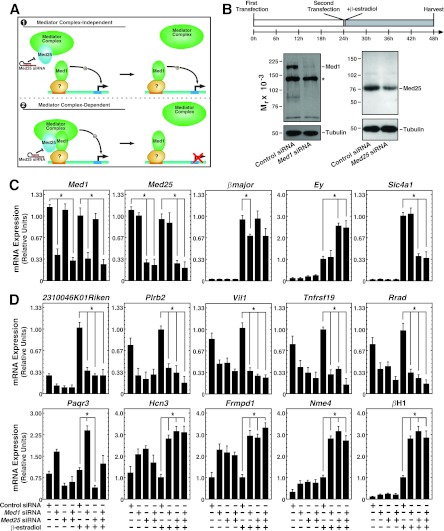
Fig 4.
Similar Med1 and Med25 requirements for transcriptional regulation in erythroid cells. (A) Potential mechanisms of Med1 function. Model 1 depicts Med1 acting independently of Mediator, while model 2 depicts Med1 bound to and utilizing Mediator (including Med25) to regulate genes. (B) (Top) Knockdown strategy. Cells were electroporated twice, allowing 24 h between electroporations, and were treated with β-estradiol (shaded rectangle) for 24 h. (Bottom) Knockdown of Med1 and Med25 proteins by siRNA transfection as measured by semiquantitative Western blotting. The asterisk indicates a nonspecific band. (C) siRNA-mediated knockdown of Med1 and Med25 mRNA and influence on GATA-1 target genes, as quantitated by qRT-PCR in G1E-ER-GATA-1 cells treated with 240 pmol control, Med1, Med25, or Med1 and Med25 siRNAs for 48 h with or without 1 μM β-estradiol for 24 h. Data are means ± standard errors for four independent experiments. *, P < 0.05. (D) Med1-regulated genes. qRT-PCR was used to quantify mRNA in G1E-ER-GATA-1 cells treated with 240 pmol control, Med1, Med25, or Med1 and Med25 siRNAs for 48 h with or without the presence of 1 μM β-estradiol for 24 h. Results are means ± standard errors for four independent experiments.