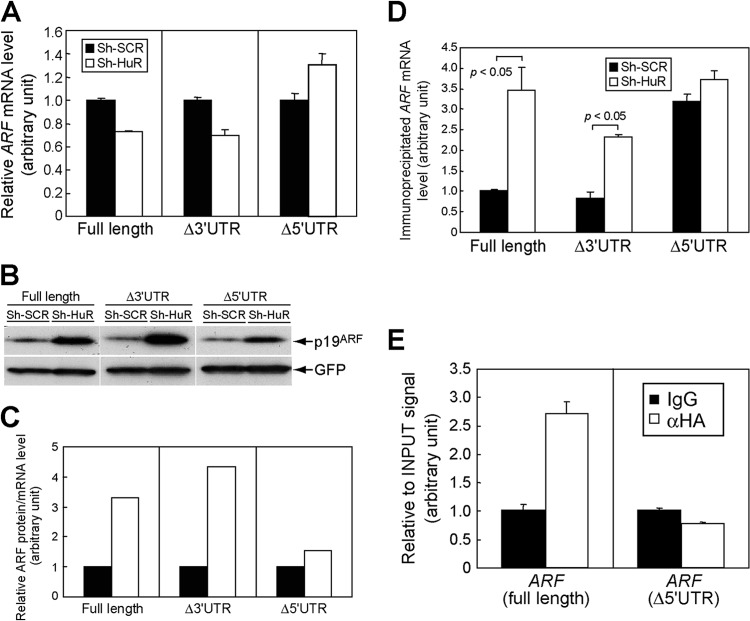
Fig 8.
HuR regulates p19ARF expression through the 5′UTR of ARF mRNA. (A) NIH 3T3 cells expressing sh-SCR or sh-HuR were transfected with plasmids bearing full-length ARF, including the 5′- and 3′UTRs (full length), ARF lacking the 3′UTR (Δ3′UTR), or ARF lacking the 5′UTR (Δ5′UTR) together with GFP expression plasmids. Three days later, total RNA was extracted and exogenous ARF expression was analyzed by real-time PCR. Values were normalized to GFP mRNA levels in each sample. (B) The cells from panel A were analyzed by immunoblotting for expression of p19ARF and GFP. (C) p19ARF levels in panel B were quantified using ImageJ, and the p19ARF level and ARF mRNA level in each sample were calculated. (D) NIH 3T3 cells expressing sh-SCR or sh-HuR were transfected with ARF expression plasmids (full length, Δ3′UTR, or Δ5′UTR) together with GFP-L10 plasmids. Three days later, cytoplasmic lysates were prepared and immunoprecipitated using GFP antibody to purify RNA-protein complexes, including GFP-L10. RNAs were recovered from immune complexes and subjected to real-time PCR analysis for ARF mRNA. Values were normalized to input signals in each sample. (E) 293T cells were transfected with ARF expression plasmids that express full-length or mutant ARF mRNA that lacks the 5′UTR (Δ5′UTR) together with HA-HuR expression plasmids. Forty-eight hours later, cells were subjected to UV cross-linking and immunoprecipitated using control or HA antibodies. Recovered RNA was analyzed by real-time PCR. Error bars represent SEM of results from triplicate samples.