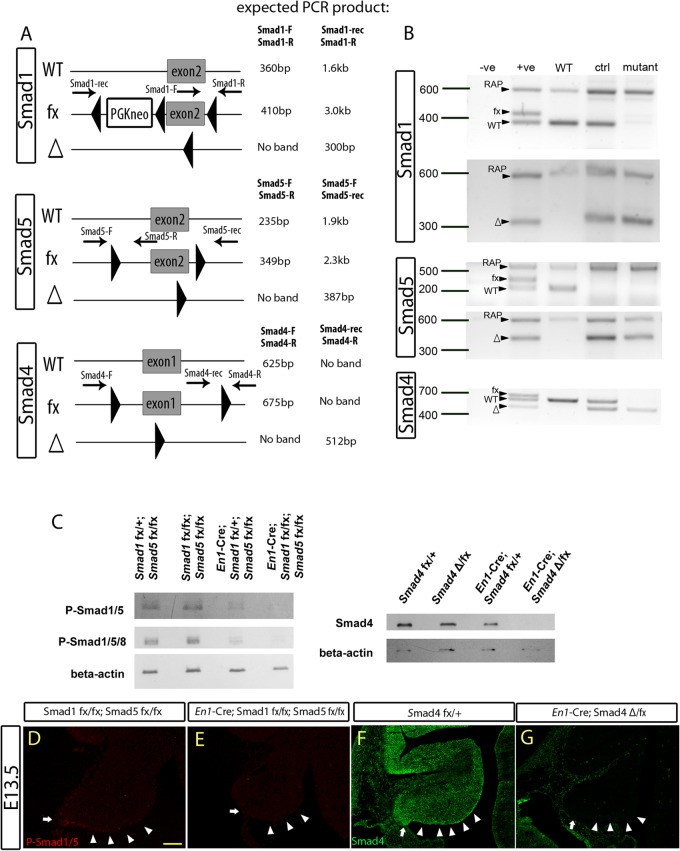
Fig 1.
En1-Cre-mediated recombination and inactivation of the conditional Smad alleles in the embryonic cerebellum. (A) Schematic diagrams showing the wild-type (WT) allele, floxed allele (fx), and Cre-recombined allele (Δ), with the locations of PCR primers and their expected product sizes indicated. (B) The PCR results for genomic DNA from E13.5 cerebella using specific primers (indicated in panel A) showed Cre-mediated in vivo recombination activities of the different targeted conditional Smad alleles in the cerebellum. (C) Western blot analysis detecting the expression of phospho-Smad1/5/8 (P-Smad1/5/8), P-Smad1/5, and Smad4 in the E13.5 cerebellum, with the genotype annotated, showing the loss of Smad protein in the corresponding mutant cerebella. (D and E) Immunofluorescence staining detecting phospho-Smad1/5 in E13.5 cerebellar sagittal sections from control (Smad1fx/fx Smad5fx/fx) (D) and Smad1/5 mutant (En1Cre/+ Smad1fx/fx Smad5fx/fx) (E) cells. Phospho-Smad1/5 expression was detected in the ARL (arrows) and parts of the ventricular zone (arrowheads) of control E13.5 cerebellum but not in the Smad1/5 mutant cerebellum. (F and G) Immunofluorescence staining detecting Smad4 on E13.5 cerebellar sagital sections from control (Smad4fx/+) (F) and Smad4 mutant (En1Cre/+ Smad4Δ/fx) (G) cells. Smad4 expression was detected in the E13.5 whole cerebellum, including the ARL (arrows) and parts of the ventricular zone (arrowheads) of the control but not in the Smad4 mutant cerebellum. Scale bar, 100 μm.