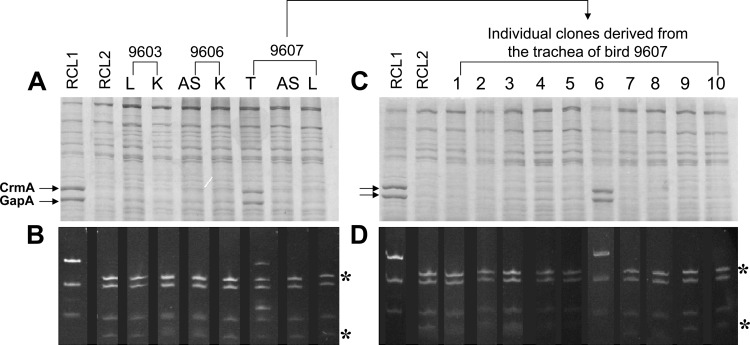
Fig 3.
Analyses of mycoplasmas recovered from RCL2-infected chickens. (A and C) Total proteins of mycoplasma populations (A) or clones (C) were separated by SDS-PAGE and stained with Coomassie blue. (B and D) Total DNAs from the mycoplasma populations (B) or clones (D) analyzed in panels A and C were subjected to a PCR assay to amplify the gapA region containing the RCL2 point mutation, and the resulting products were digested with MseI. Restriction fragments were detected by ethidium bromide staining after agarose gel electrophoresis. Mycoplasma populations were recovered from the left air sacs (AS), the tracheae (T), the lungs (L), or the kidneys (K) of RCL2-infected chickens as described in Materials and Methods. Numbers above the lanes correspond to the number that was assigned to each bird. RCL2 and RCL1, two isogenic variants derived from Rlow that differ by (i) their HA phenotype, (ii) the expression of GapA and CrmA, and (iii) a base substitution at the beginning of the gapA gene, were used as controls. Lanes 1 to 10 correspond to individual clones randomly selected from the mycoplasma population collected from the trachea of bird 9607. Asterisks indicate restriction DNA fragments that are detected only in HA− RCL2 variants lacking the GapA and CrmA products.