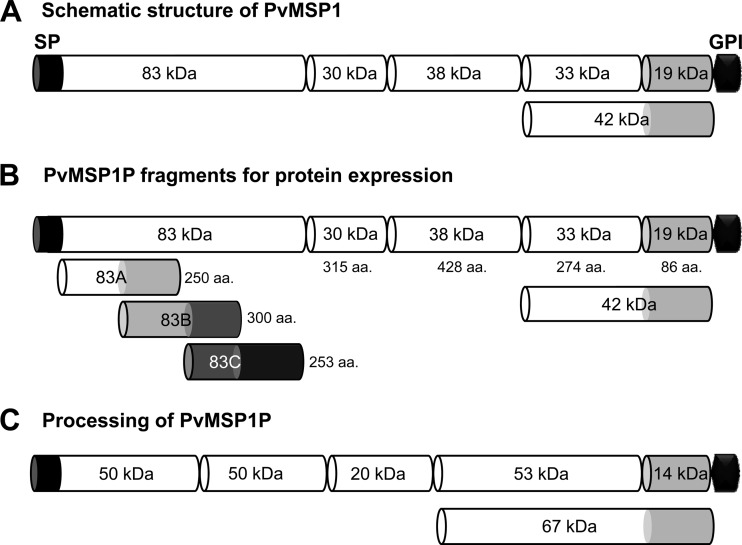
Fig 1.
Schematic diagram of PvMSP1, fragments of PvMSP1P for recombinant protein expression, and processing of native PvMSP1P. (A) Schematic diagram of processing of PvMSP1. (B) Demarcation of PvMSP1P, similar to the processed forms of PvMSP1, for protein expression of 8 fragments of PvMSP1P. For the N-terminal 83-kDa region, three 50-amino-acid overlapping fragments were expressed as 83A, 83B, and 83C. The MSP1P protein comprises 1,856 amino acids, with a calculated molecular mass of 214.5 kDa. The predicted signal peptide (SP; aa positions 1 to 28) and GPI anchor signal (GPI; aa 1835–1854) are shown. Eight fragments of MSP1P (83A [aa 29 to 278], 83B [aa 229 to 528], 83C [aa 479 to 731], 30 [aa 732 to 1046], 38 [aa 1047 to 1474], 42 [aa 1475 to 1834], 33 [aa 1475 to 1748], and 19 [aa 1749 to 1834]) were expressed as recombinant proteins. PvMSP1P-30, -42, -33, and -19 were used to raise specific antisera. (C) Hypothetical processing of PvMSP1P was predicted from Western blot results of the parasite lysate probed with anti-PvMSP1P-42 serum (Fig. 3B). aa, amino acid; kDa, kilodalton; SP, signal peptide; GPI, glycophosphatidylinositol anchor signal.