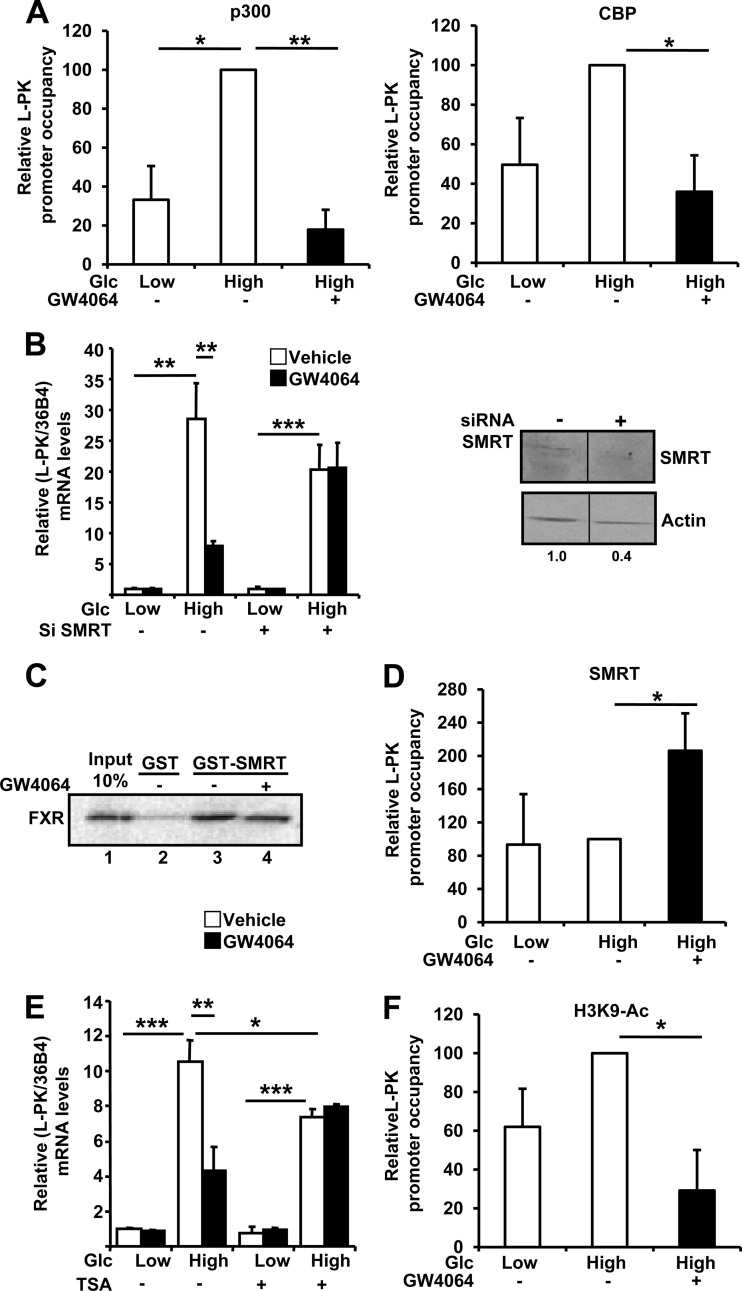
Fig 4.
FXR activation leads to the release of coactivators p300 and CBP and the recruitment of the coinhibitor SMRT on the L4L3 region at high glucose concentration. (A) Relative levels of L-PK promoter occupancy by p300 and CBP on the L4L3 region. (B) Effects of SMRT gene silencing on L-PK mRNA (left) and SMRT protein (right) levels in IHH transfected with specific siRNAs and incubated for 24 h at low (1 mM) or high (11 mM) glucose concentration and with vehicle (DMSO) or GW4064 (5 μM). Proteins were extracted and analyzed as indicated in Materials and Methods. SMRT protein levels were quantified by densitometry and normalized to actin protein level. (C) In vitro GST pulldown experiments using full-length GST-SMRT and TNT FXR in the presence of [35S]methionine. (D) Relative levels of L-PK promoter occupancy by SMRT. (E) Effects of TSA treatment on L-PK gene expression in IHH incubated for 24 h at low (1 mM) or high (11 mM) glucose concentration and with vehicle (DMSO) or GW4064 (5 μM). (F) Relative levels of H3K9 acetylation of L-PK. For the experiments whose results are shown in panels A, D, and F, the occupancies were evaluated by quantitative PCR in ChIP experiments performed using total extracts from IHH incubated for 5 h in a medium containing low (1 mM) or high (11 mM) glucose concentrations and vehicle (DMSO) or GW4064 (5 μM). Occupancies are expressed relative to those at low glucose concentration with vehicle, arbitrarily set to 1. Each experiment was performed at least 3 times, and the results are the averages and standard deviations of these experiments. For the experiments whose results are shown in panels B (left) and E, L-PK and control 36B4 mRNA levels were measured by real-time quantitative PCR. The values are expressed relative to those at low glucose concentration with vehicle, which were arbitrarily set to 1.