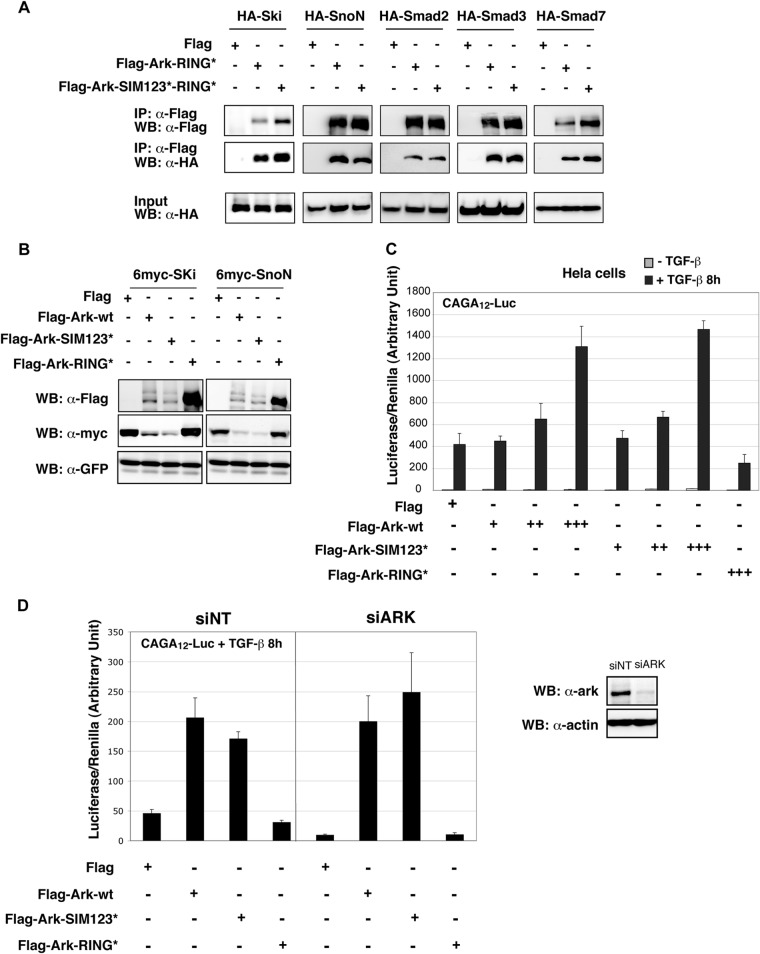
Fig 2.
Arkadia SIMs are not essential for TGF-β signaling activation. (A) SIMs are not necessary for the interaction of Arkadia with its different partners in the TGF-β pathway. HEK293 cells were cotransfected with the indicated combination of Flag-Ark-RING* or Flag-Ark-SIM123*-RING* and plasmids expressing HA-tagged Ski, SnoN, Smad2, Smad3, and Smad7. Flag immunoprecipates were analyzed by Western blotting using anti-Flag and anti-HA antibodies. The corresponding whole-cell lysates (input) were analyzed using anti-HA antibody. (B) The SIMs of Arkadia are not necessary for SnoN and Ski degradation. HEK293 cells were transfected with 6-myc–SnoN or 6-myc–Ski together with Flag-Ark-wt, Flag-Ark-SIM123*, or Flag-Ark-RING* and along with a GFP expression vector as an internal control for transfection. Whole-cell lysates were analyzed with anti-Flag, anti-myc, and anti-GFP antibodies. (C and D) Arkadia SIMs are not necessary for Smad-dependent transcription on a synthetic reporter. HeLa cells were transfected with CAGA12-Luc together with TK-Renilla and Flag-Ark-wt, Flag-Ark-SIM123*, or Flag-Ark-RING*, as indicated. TGF-β was added or not 8 h before lysis and measurement of luciferase and Renilla activities. Experiments were done in triplicate and repeated three times. (D) Cells were transfected with a nontarget siRNA (siNT) or siRNA targeting Arkadia (siArk) 48 h prior to plasmid transfection. Arkadia knockdown efficiency was evaluated by Western blotting on whole-cell extracts using anti-Ark antibody, as shown on the right. Actin was used as a loading control.