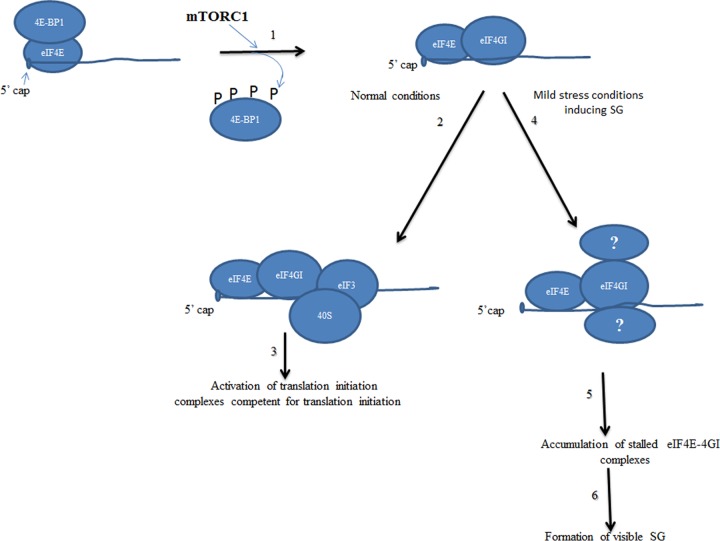
Fig 7.
Our working model of mTORC1-eIF4E-4GI-dependent mode of SG assembly. Under both normal and SG-inducing stress conditions, mTORC1 drives formation of eIF4E-eIF4GI translation initiation complexes through phosphorylation of its 4E-BP1 target (1). Under normal growth conditions, eIF4E-4GI complexes are joined by 40S ribosomes at an early step of translation initiation (2 and 3). Under mild stress conditions inducing SG, eIF4E-4GI complexes may serve as scaffolding for the recruitment of unidentified factors in an mTORC1-dependent manner (4). This binding then stalls eIF4E-4GI complexes in an inactive status (5) and results in accumulation leading to formation of SG (6).