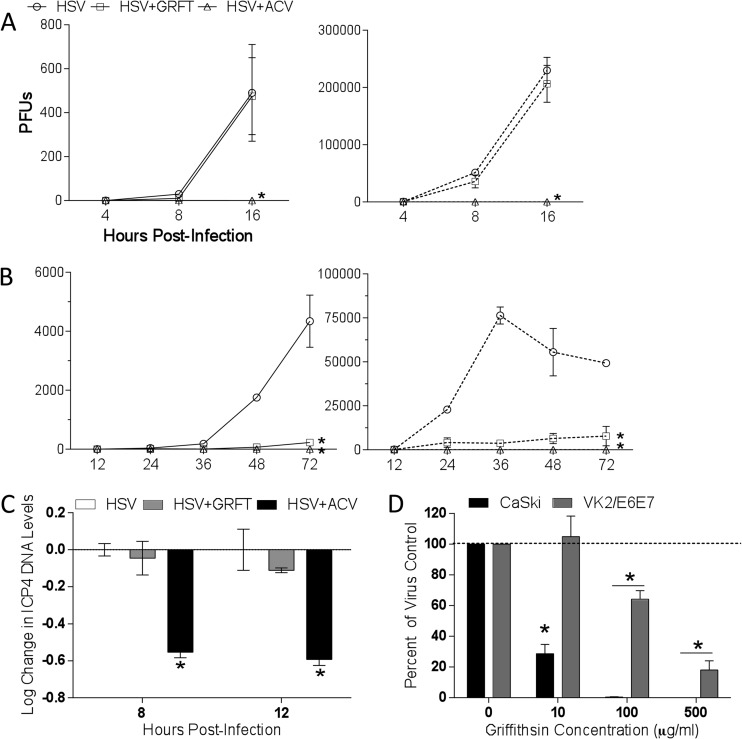
Fig 2.
Griffithsin inhibits cell-to-cell spread of HSV-2. (A) One-step growth of HSV was quantified by infecting CaSki cells with an MOI of 5 and then adding GRFT or ACV to the overlay media. At 4, 8, and 16 hpi, supernatants and cells were harvested and, after cells were freeze-thawed three times, viral growth was quantified by determining the titers of the supernatants (solid lines) or cells (dotted lines) on Vero cells. (B) To assess multistep growth, CaSki cells were infected with an MOI of 0.01, and drug was added to overlay media as described for panel A, and then at 12, 24, 36, 48, and 72 hpi, supernatants and cells were again harvested and titers were determined on Vero cells. Data shown are from two experiments conducted in duplicate. Asterisks indicate significance compared to no drug using two-way ANOVA. (C) CaSki cells were infected with HSV-2 at an MOI of 1 with GRFT, ACV, or no drug (control) added to the overlay media. Cells were harvested 8 or 12 hpi, and DNA was extracted and run in real-time PCR. Data are presented as means ± SEM of log change in ICP4 DNA levels relative to infected cells without drug, controlling for RPLPO as the housekeeping gene. Asterisk represents significance compared to HSV without drug using unpaired t test, P < 0.05. (D) Cells were infected with HSV-2 for 4 to 5 h, after which time they were trypsinized and cocultured with uninfected cells in medium supplemented with pooled human IgG and GRFT for 48 h to allow plaques to form. Data are shown as means + SEM of percentage of virus control from three independent experiments. Asterisks indicates significance from virus control (no GRFT) using unpaired t test, P < 0.05.