Fig 2.
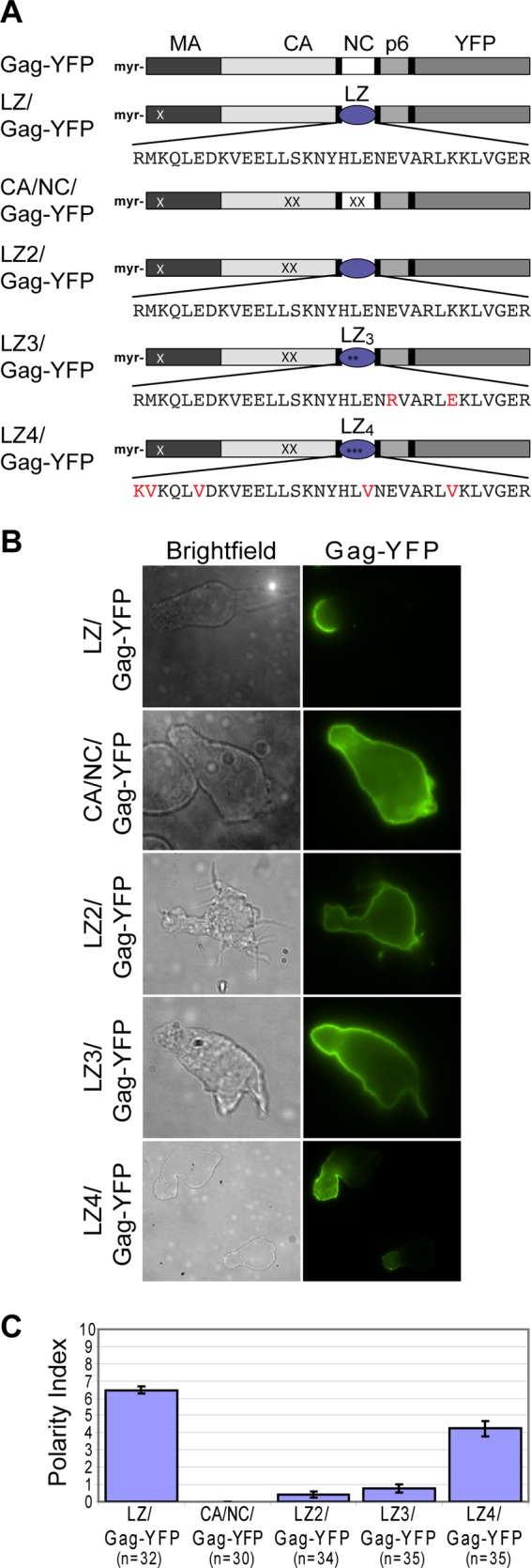
LZ4/Gag-YFP polarizes more extensively than CA/NC/Gag-YFP, LZ2/Gag-YFP, or LZ3/Gag-YFP. (A) Illustration of Gag derivatives containing leucine zipper (LZ) sequences in place of NC. LZ/Gag-YFP is a prototype LZ-containing Gag that multimerizes and forms particles efficiently. Red letters in LZ sequences and asterisks denote mutations that are expected to convert dimeric LZ into trimeric (LZ3) or tetrameric (LZ4) ones. The CA mutation, WM184,185AA (WMAA; denoted by XX in CA), which prevents CA-mediated dimerization, was introduced into the LZ2/Gag-YFP, LZ3/Gag-YFP, and LZ4/Gag-YFP constructs so that LZ sequences provide the only major Gag-Gag interaction activity in these constructs. In CA/NC/Gag-YFP, the 14A1G change was introduced into NC (all NC basic residues substituted with Ala or Gly; denoted by XX in NC) in addition to the WMAA change to eliminate major Gag-Gag interaction domains. All constructs contain the MA mutation 20LK (denoted by a white X in MA), which increases membrane binding. (B) CA/NC/Gag-YFP, LZ2/Gag-YFP, LZ3/Gag-YFP, LZ4/Gag-YFP, and LZ/Gag-YFP were expressed in P2 cells via infection with VSV-G-pseudotyped viruses encoding these Gag constructs. (C) The Gag polarity index was determined for the mutants in polarized P2 cells as described in Materials and Methods. n, the number of cells used for quantification. Error bars represent standard errors of the means.
