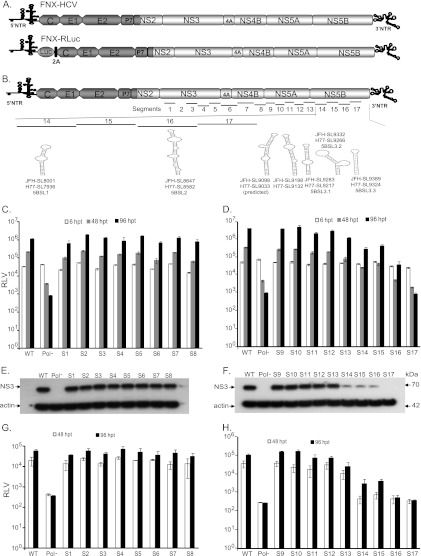
Fig 2.
RNA cis element analysis of the HCV nonstructural-protein-coding region. (A) Schematic diagram of hepatitis C viruses used in this study. FNX-HCV is a synthetic version of a genotype 2a J6CF and JFH-1 chimera (the J6CF strain region is shown in dark gray, including the 5′ NTR, and the JFH-1 strain region is shown in light gray). A monocistronic Renilla luciferase (luc) reporter virus (FNX-Rluc) based on the J6/JFH chimeric virus is shown. The luciferase gene is fused in frame with the core gene through foot and mouth disease virus 2A sequence. (B) Schematic representation of the HCV genome showing the locations of 17 mutated segments in the nonstructural-protein-coding region. The stem-loop structures described in the NS5B region corresponding to the genome positions of JFH-1 and H77 are noted. (C and D) Analysis of viral genome replication of mutant reporter viruses. Huh-7.5.1 cells were electroporated with 10 μg of in vitro-transcribed genomic RNA of wild-type FNX-Rluc reporter virus and individual S1 to S17 mutant reporter viruses. A control reporter virus with nonfunctional polymerase activity (Pol−) is included. The transfected cells were lysed at 6, 48, and 96 h p.t. using Promega Renilla luciferase assay lysis buffer, and the levels of Renilla luciferase were quantified. The experiment was performed in triplicate. The mean Renilla luciferase values (RLV) with standard deviations are shown in log10 scale as a bar graph. The replication-deficient mutant S17 showed luciferase activity similar to that of the Pol− control virus. At 96 h p.t., mutant viruses S14, S15, S16, and S17 had significant reductions in genome replication compared to that of wild-type virus (P value < 0.0001 by unpaired t test). (E and F) Western blot of the expression of HCV protein. The 70-kDa NS3 antigen was detected from the protein lysates obtained at 96 h posttransfection by primary mouse monoclonal antibody and secondary goat-anti mouse IgG conjugated with HRP. As a loading control, β-actin was included. (G and H) Infectivities of mutant viruses. Naïve Huh-7.5.1 cells were infected with the cell-free supernatants harvested at 48 and 96 h posttransfection. Renilla luciferase activities were measured from the lysates harvested at 48 h postinfection. The mean RLV with standard deviations are depicted in the bar graph. Mutant reporter viruses S13, S14, S15, S16, and S17 exhibited significant reductions in infectivity at 48 h p.t. (P value ≤ 0.005) and 96 h p.t. (P value < 0.005) compared to that of wild-type virus. The experiment was repeated three times, and data from a representative experiment are shown.