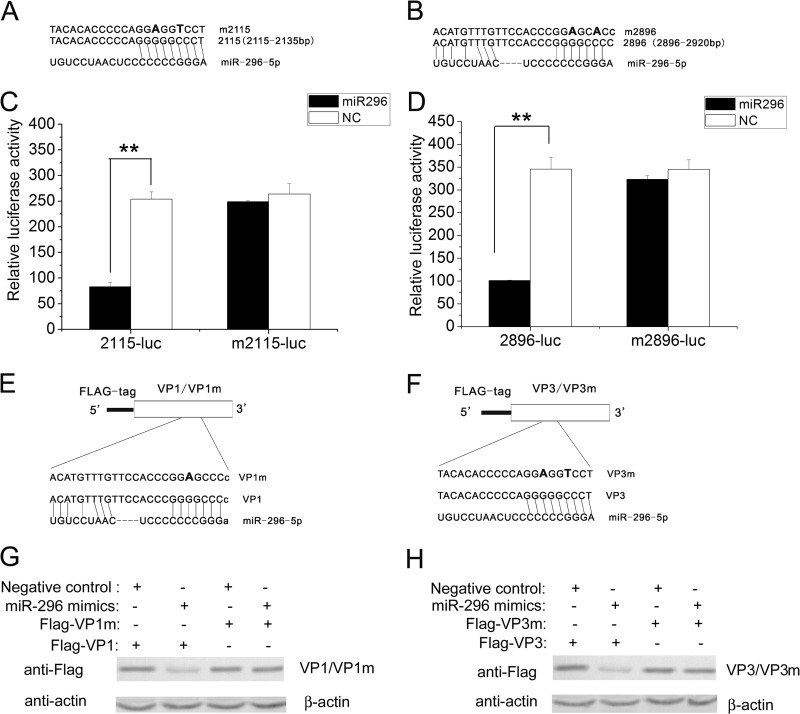
Fig 4.
Targeting of EV71 genomic RNA sequence by hsa-miR-296-5p. (A, B) The complementary sequences of two hsa-miR-296-5p candidate target “seed sequences” and mutated forms are indicated. Mutated nucleotides are bolded. The complementary sequences are from the EV71-BrCr-TR strain (GenBank number AB204852). (C, D) Luciferase reporter plasmids containing the hsa-miR-296-5p target sites (2115-luc and 2896-luc) and corresponding mutants (m2115-luc and m2896-luc) were cotransfected with the plasmid pRL-TK into hsa-miR-296-5p- or NC-treated RD cells. Reporter activities were determined 24 h posttransfection by dual-luciferase assays, and the resultant ratios are shown. Data are representative of at least two independent experiments, with each determination performed in triplicate (mean ± SD of fold change). *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01. (E, F) Schematic representation of constructs Flag-VP1 and Flag-VP3 and corresponding constructs Flag-VP1m and Flag-VP3m containing mutations in hsa-miR-296-5p target sites. (G, H) Western blot analysis of effects of hsa-miR-296-5p on expression of EV71 VP1 and its mutant VP1m (G) and VP3 and its mutant VP3m (H). RD cells were transfected with the indicated plasmids in the presence of hsa-miR-296-5p or randomized NC. Proteins were analyzed with an anti-FLAG antibody with β-actin as the internal control.