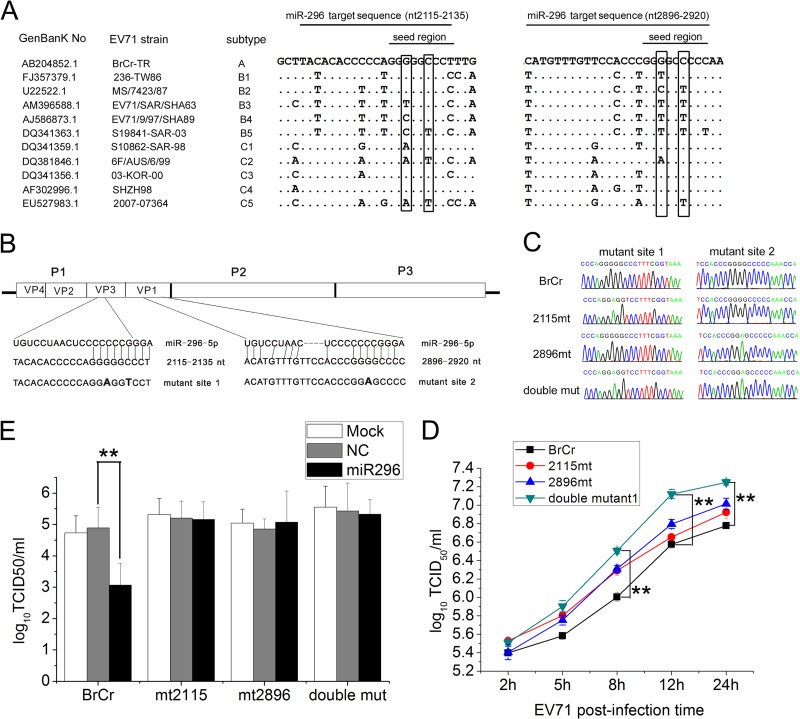
Fig 5.
Effects of synonymous mutations in hsa-miR-296-5p target sites on EV71 replication and inhibitory effects of hsa-miR-296-5p on EV71. (A) Genomic sequence alignment of EV71 strains of different subtypes. Synonymous nucleotide mutations in the seed region of the two hsa-miR-296-5p target sites are boxed. (B) Schematic representation of pEV71(BrCr-TR) constructs with the hsa-miR-296-5p target sites and their corresponding mutants. (C) Sequencing results of each mutant EV71 virus at mutation sites. (E) Effects of hsa-miR-296-5p on infectivity of WT (BrCr) and mutant (mt2115, mt2896, and double mutant) viruses. hsa-miR-296-5p-transfected RD cells were infected with each virus at an MOI of 5. Viral titers were determined at 12 h postinfection. Data are representative of at least two independent experiments, with each determination performed in triplicate (mean ± SD of fold change). **, P < 0.01. (D) Growth curves of WT and mutant viruses. SK-N-SH cells were infected with each virus at an MOI of 5, and EV71 titers of infected cells were determined. Data are representative of at least two independent experiments, with each determination performed in triplicate (mean ± SD of fold change). **, P < 0.01.