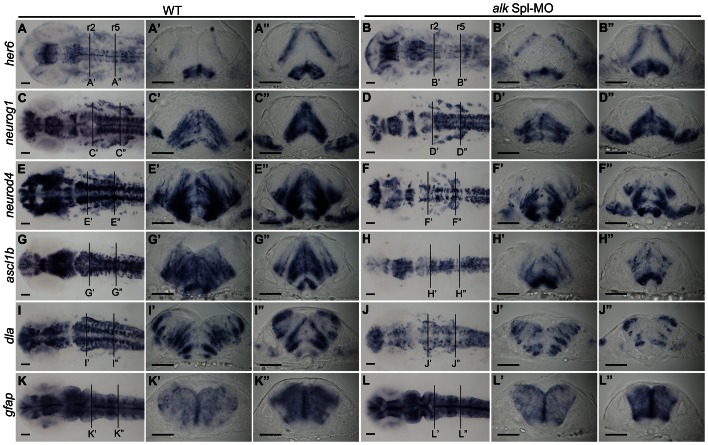
Figure 5. Knock-down of alk impairs neuronal differentiation.
(A–L) In situ hybridization of neuronal marker genes with wild-type (A,C,E,G,I,K), and alk Spl-MO injected embryos (B,D,F,H,J,L) at 22 hpf. Images in first row show dorsal views of head region with anterior to the left. (A′–L′,A″ –L″) Transverse cross sections at the level of r2 (A′–L′) and r5 (A″ –L″) in WT embryos or alk Spl-MO injected morphants. (A,A′A″,B,B′B″) her6 expression was unchanged in alk morphants compared to WT. (C,C′,C″,D,D′,D″) neurog1 expression was unchanged or only slightly reduced in morphants. (E,E′,E″,F,F′,F″) neurod4 expression was strongly reduced in morphants in several regions including the hindbrain. (G,G′,G″,H,H′,H″) Similarly, ascl1b expression in alk morphants was also significantly reduced. (I,I′,I″,J,J′,J″) dla expression in alk morphants was also reduced. (K,K′,K″,L,L′,L″) Glia marker gfap expression was unchanged. Scale bars: 50 µm. Lines at r2 and r5 indicate levels of cross sections.