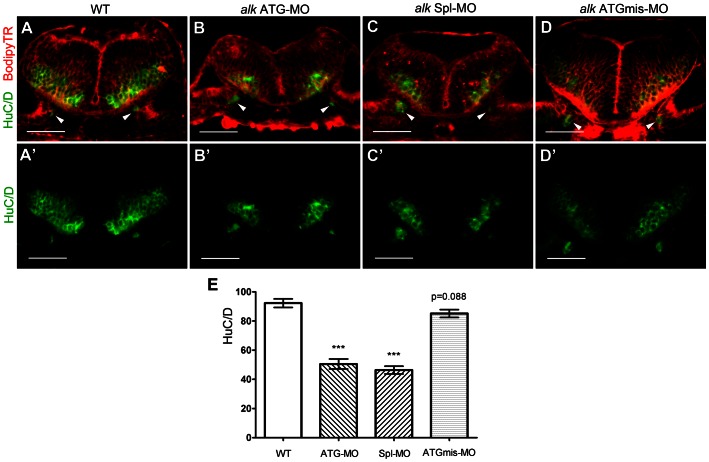
Figure 7. Knock-down of alk reduces the number of differentiated hindbrain neurons.
(A–D) Confocal sections of 31 hpf embryos at r5 level immunostained with the pan-neuronal marker HuC/D (green) and co-stained with bodipy-Texas Red (TR, red). The HuC/D channel (green) is separately shown in (A′–D′). Arrowheads point to emerging neurons in the ear, serving as landmark to indicate that all sections were at the same position. In both alk ATG-MO (B,B′) or alk Spl-MO (C,C′) injected embryos, the areas of postmitotic neurons were clearly smaller than in WT (A,A′) or alk ATGmismatch-MO injected embryos (D,D′). The proliferative ventricular and subventricular zones were normal in size. (E) Y-axis indicates numbers of HuC/D expressing cells on sections. Both alk ATG-MO and alk Spl-MO groups were significantly different from WT (***p<0.001), whereas the change in alk ATGmismatch-MO group was not significant (p = 0.088). Mean ± SEM, N = 12 in WT and ATG-MO, N = 14 in Spl-MO and ATGmismatch-MO. Unpaired two tailed t-test. Scale bars: 50 µm.