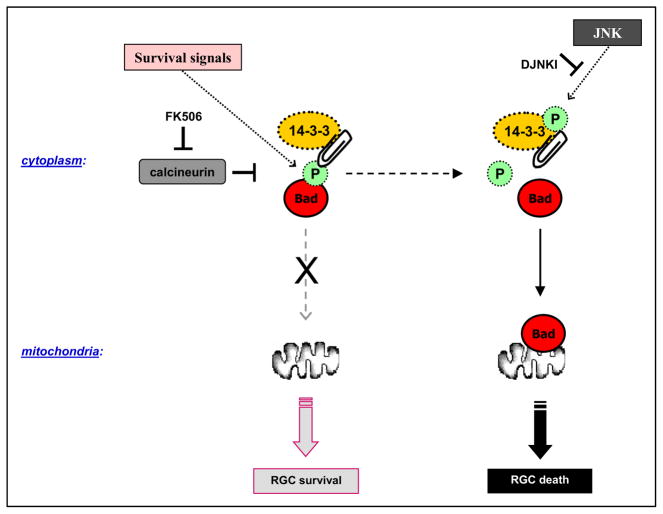
Figure 5.
Targeted proteomics analysis of experimental rat glaucoma. As an effort to explore specific protein interactions in an experimental rat model of glaucoma, 14-3-3-containing retinal protein complexes were eluted using co-immunoprecipitation and recombinant protein-based affinity pull-down for subsequent analysis by mass spectrometry. Based on the proteomics data and in vivo treatment experiments in rats, 14-3-3 proteins were found to control the subcellular localization of and function of Bad in a phosphorylation-dependent manner, and thereby constitute an important regulatory pathway of RGC death signaling during glaucomatous neurodegeneration. This flow diagram has recently been published (Yang et al., 2008).