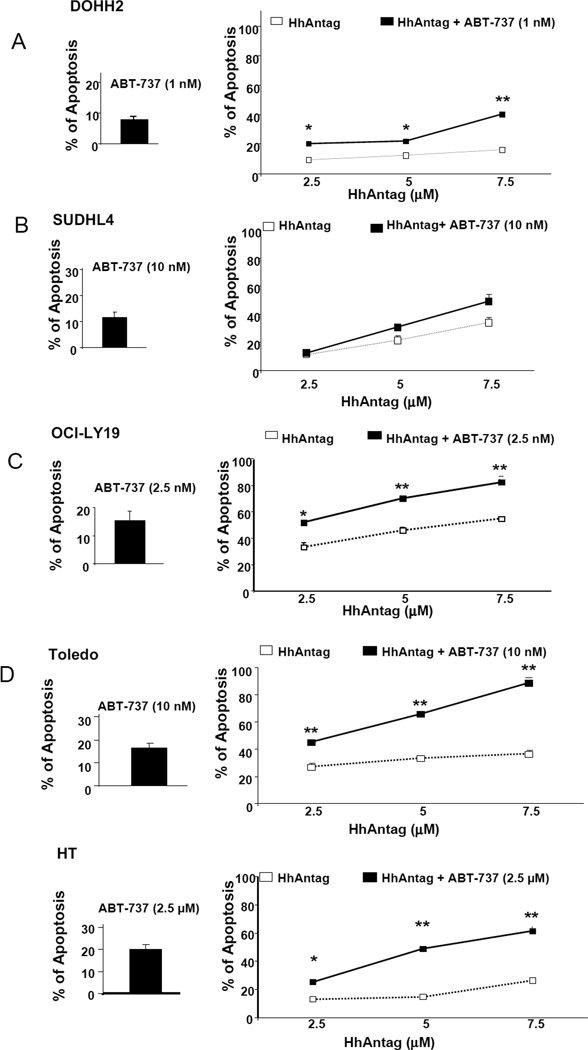
Figure 2. Combining low-doses of ABT-737 and increasing concentrations of HhAntag resulted in increased apoptosis in GC-DLBCL cells.
Annexin V and PI labeling assay showed that the combined treatments of fixed IC20 doses of ABT-737 and increasing concentrations of the HhAntag resulted in a statistically significant increase of apoptosis in comparison to treatments with HhAntag alone in 4 of 5 cell lines, DOHH2 (A), HT (C), OCI-Ly19 (D) and Toledo (E). A significant increased in apoptosis combining ABT-737 with HhAntag was not detected SuDHL4 (B). Similarly that with the MTT assays, DOHH2 and HT were the cell lines showing the lowest sensitivity to the treatments with the HhAntag alone. The percentage of apoptosis induced by the concentrations of ABT-737 used for the combinatorial treatments is shown in the left panels (all of them were below 20%). * p<0.05; **p<0.01.