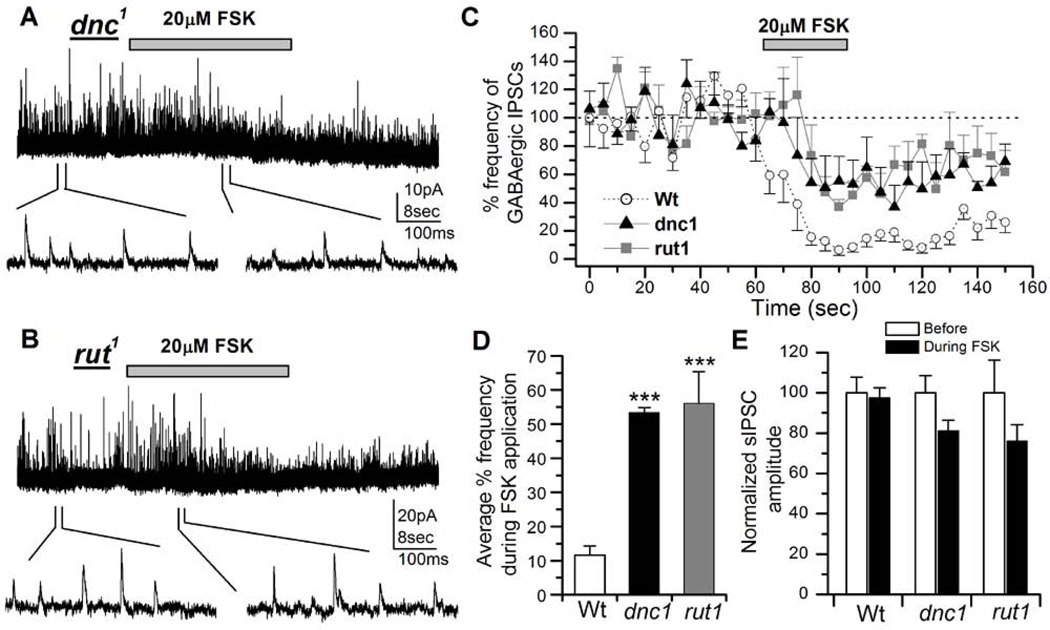
Figure 7. Modulatory actions of forskolin (FSK) on inhibitory GABAergic postsynaptic currents (IPSCs) is attenuated in learning and memory mutants.
A, Effects of FSK on GABAergic IPSCs in a dnc1 neuron. After obtaining a stable IPSC trace from a 3 day old dnc1 neuron, 20µM FSK was focally applied for 30 seconds (indicated by bar). FSK suppression of GABAergic IPSC frequency was significantly attenuated compared to wild type (see Figure 1). GABAergic IPSCs are shown on an expanded time scale below the entire recording trace. VH = 0 mV. B, Effects of FSK on GABAergic IPSCs in a rut1 neuron (3 days old). C, The graph shows a comparison of the reduction of GABAergic IPSCs by 20µM FSK in wild type (n=9, circles), dnc1 (n=5, triangles) and rut1 (n=7, squares) neurons. D, The graph shows reduction in percent frequency of GABAergic IPSCs during the focal application of 20µM FSK in dnc1 and rut neurons compared to wild type. Bars indicate SEM. Students t-test, ***P< 0.001. E, The graph shows average sIPSC amplitude before and during FSK application from GABAergic IPSCs described in C. Although the amplitude in dnc1 and rut1 was slightly reduced the difference was not significant. Paired T-test was used to compare before and after treatment amplitudes in each genotype.