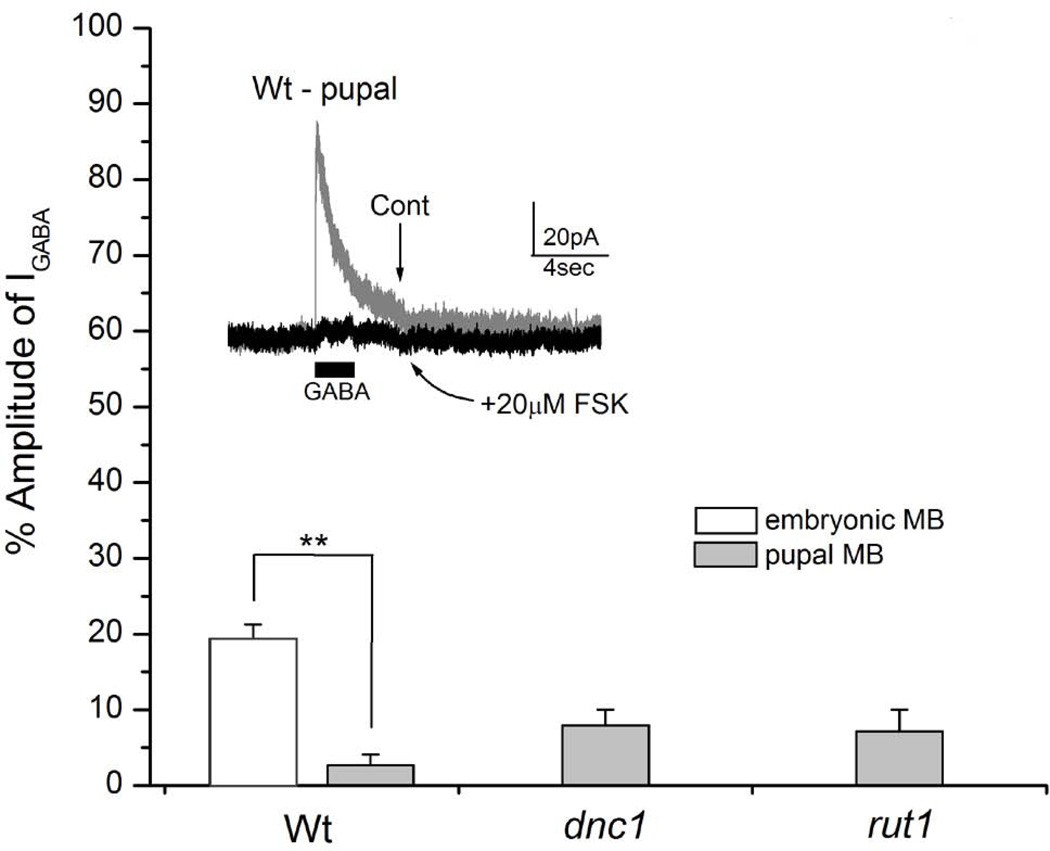
Figure 9. 20µM forskolin (FSK) markedly suppresses GABA-evoked currents (IGABA) recorded in wild type, dnc1 and rut1 pupal mushroom body (MB) neurons.
Cultured pupal MB neurons were prepared from wild type, dnc1 and rut1. MB neurons were identified by GFP expression under the control of a MB-specific driver c309-Gal4. GABA-evoked currents (IGABA) were suppressed in neurons derived from all three strains. Suppression for wild type, dnc1 and rut1 was 97.3, 92.0 and 92.9%, respectively. Although this suppression was slightly higher in wild type, there was no statistical difference between the three strains. In contrast, GABA-evoked currents (IGABA) from wild type embryonic MB neurons showed reduced sensitivity to FSK as it suppressed only 80.7%. Inset IGABA recorded from a wild type pupal MB neurons before and after 20µM FSK perfusion. Students t-test, **P< 0.01. Number of replicates: Wt embryonic (n=7) and pupal (n=4), dnc1 (n=4), rut1 (n=6).