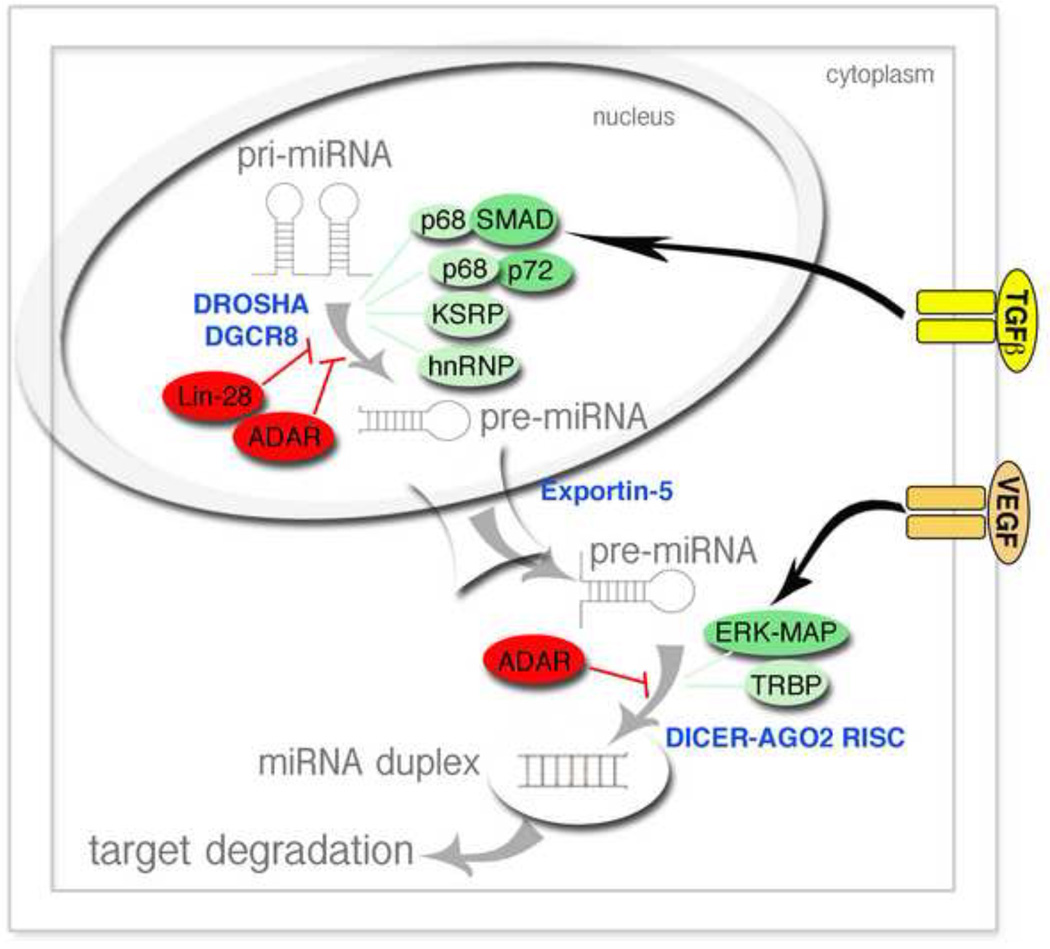
Figure 1. miRNAs processing and regulation.
miRNA precursors (pri-miRNA) are processed by DROSHA and DGCR8 proteins into smaller RNA hairpins named pre-miRNAs. Protein-protein or RNA binding proteins are able to inhibit (Red) or promote (Green) pri-in to pre-miRNA processing with the nucleus. After export to the cytoplasm, pre-miRNAs are associated with the endo nuclease DICER and other regulatory protein such as TRBP. DICER cleaves the pre-miRNAs in a ~22 nt duplex miRNA which is incorporated in the RNA-Inducing–Silencing–Complex (RISC) where the mature miRNA associates with AGO2 to induce translation repression of the target mRNA. This process can be regulated by several growth factor singling pathways through ERK-MAP kinase or SMAD activation. hnRNP= heterogeneous nuclear riboprotein; KSRP= KH-type splicing regulatory protein; SMAD=mothers against decapentaplegic homolog; ADAR=adenosine deamenases acting in RNA.