Figure 4.
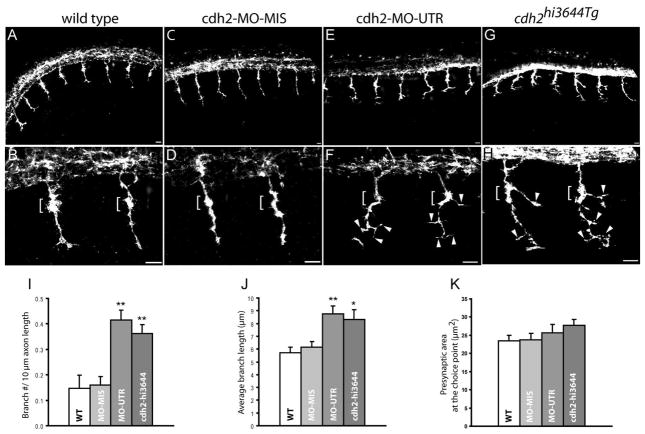
Loss of N-cadherin expression affects primary motor axons branching. A – H) Lateral views of 24 hpf zebrafish embryos immunostained with SV2 and znp1 antibodies, and observed under confocal microscopy. A, B) Primary motor axons in wild type embryos exited the spinal cord and grew ventrally towards the horizontal myoseptum. The axons are enlarged at the area of contact with the muscle pioneer cells (brackets in B and D). C, D) Zebrafish embryos injected with N-cadherin antisense mismatched morpholinos (cdh2-MO-MIS) display axonal morphologies similar to wild type embryos. E, F) Embryos injected with antisense N-cadherin morpholino (cdh2-MO-UTR) reached the horizontal myoseptum but grew aberrant branches at the choice point (brackets) and in the ventral myotome (arrowheads). An axon branch is an extension of the axon from the center of the axon shaft >3 μm long. G, H) In cdh2hi3644Tg homozygote embryos, motor axons formed aberrant branches at the choice point (brackets) and ventral to the horizontal myoseptum (arrowheads). I) Analysis of the number of branches per 10 μm of axon expressed as mean ± SE (wild type n = 27; cdh2-MO-MIS n = 29; cdh2-MO-UTR n = 26; cdh2hi3644Tg n = 26 (n, number of axons analyzed). H) Analysis of the average length of the branches expressed as mean ± SE (wild type n = 21; cdh2-MO-MIS n = 27; cdh2-MO-UTR n = 51; cdh2hi3644Tg n = 47 (n, number of branches examined)). Analysis of the presynaptic surface area at the choice point expressed as mean ± SE (wild type n = 48; cdh2-MO-MIS n = 44; cdh2-MO-UTR n = 31; cdh2hi3644Tg n = 29 (n, number of axons examined)). T-test comparison of mutant and morpholino injected embryos versus wild type samples, ** p < 0.005, * p < 0.05. Scale bars, 10 μm. WT; wild type. Rostral is to the left and dorsal is to the top.