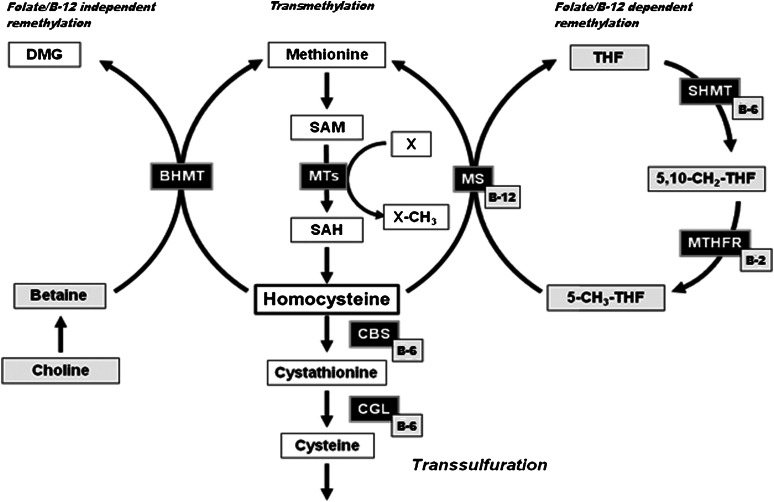
Figure 1.
Hepatic folate, methyl group, and homocysteine metabolism. For this review, important SAM-dependent methyltransferases include glycine N-methyltransferase (GNMT), guanidinoacetate N-methyltransferase (GAMT), and phosphatidylethanolamine N-methyltransferase (PEMT). These 3 methyltransferases respectively catalyze the conversion of glycine to sarcosine, guanidinoacetate to creatine, and phosphatidylethanolamine to phosphatidylcholine. In addition to folate, these reactions are dependent on a number of other B vitamins, including riboflavin (vitamin B-2), vitamin B-6, and vitamin B-12. Metabolites and enzymes: BHMT, betaine-homocysteine S-methyltransferase; CBS, cystathionine β-synthase; CGL, cystathionine γ-lyase; DMG, dimethylglycine; MS, methionine synthase; MTs, methyltransferases; MTHFR, 5,10-methylene-THF reductase; SAH, S-adenosylhomocysteine; SAM, S-adenosylmethionine; SHMT, serine hydroxymethyltransferase; THF, tetrahydrofolate; X, methyl acceptor. Adapted from reference (5) with permission.